Aluminum holds an important place in the machining industry and is the preferred choice for a variety of industrial applications due to its superior light weight, high strength, corrosion resistance and ease of machining. Aluminum is widely used not only in aerospace, automotive manufacturing and construction, but also in electronics, medical devices and consumer products.
Its good electrical and thermal conductivity properties make it an excellent performer in heat sinks, electronic enclosures and cables.During machining, the malleable and easy-to-cut properties of aluminum allow for complex geometries and precise machining tolerances.
Common Types of Aluminum


Excellent fatigue properties and crack extension resistance, suitable for high load use environment.

Good ductility and plasticity, superior processing performance, suitable for deep-drawing and spin molding.

Suitable for various machining processes such as turning, milling, drilling and cutting, and high surface quality after machining.

Series 7 aluminum is one of the strongest of all aluminum alloys and is well suited for applications with high strength requirements.
It has high strength, especially after cold working. Good ductility and plasticity, suitable for a variety of molding processes.

One of the strongest of the non-heat-treated aluminum alloys. It has excellent corrosion resistance especially in marine and industrial environments.

Moderate strength for structural applications. Good corrosion resistance in a wide range of environments, especially in architectural and decorative applications.

High strength, especially for structural applications with high strength requirements. Suitable for machining, especially for milling and turning processes.
Advantages of Aluminum
- Superior Lightweight
Aluminum has a density of approximately 2.7 g/cm³, about one-third the density of steel, making it ideal for lightweight applications.
Excellent Surface Finishing Properties
Various surface treatments, aluminum can be sublimated, anodizing, powder coating, and wet painting to enhance aesthetics and durability. - Good Electrical Conductivity
Aluminum has about 60% of the electrical conductivity of copper, but because of its low density, its conductivity per unit mass is close to that of copper, making it widely used in power transmission and distribution systems. - Excellent Processability
Easy to process, aluminum and its alloys are easy to carry out a variety of processing techniques, including forging, casting, rolling, extrusion, stretching and so on.
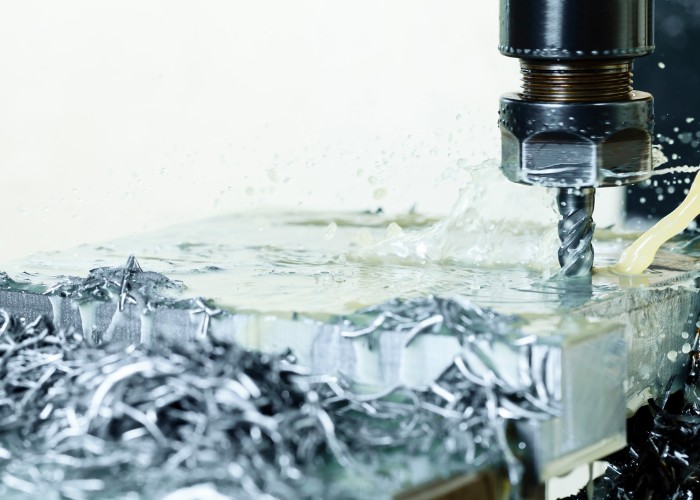


Aluminum Processing Technology
- CNC Machining
CNC machining can produce a wide range of complex shapes and designs. This makes it ideal for custom and specialized aluminum parts. - Wire EDM
Wire EDM does not make physical contact with the workpiece. This avoids any mechanical stress or deformation to the material, making it ideal for delicate or complex shapes. - Laser Cutting
High-energy laser beams are used to cut aluminum materials with high processing precision for aluminum parts with complex shapes and high requirements.
Applicable Surface Finishes
- Anodizing
Through electrochemical methods to generate a layer of oxide film on the surface of aluminum, with good corrosion resistance, wear resistance and decorative, but also can be dyed to give aluminum products a variety of colors. - Laser Engraving
Laser engraving produces a logo or pattern that is permanent and has a superior textured appearance. - Sandblasting
Sandblasting effectively removes oxidation, oil and other contaminants from aluminum surfaces. Enhance the appearance and texture of the final product.

Performance Parameters of Aluminum
| Performance Indicators | Numerical Value |
| Intensity | 2.70 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | 660.3°C |
| Hardness (Shore D) | 15-150 HB |
| Heat distortion temperature | 350-500°C |
| Water absorption | 0.1-0.2 |
| Tensile strength | 70-700 MPa |
| Yield strength | 35-500 MPa |
| Elongation | 1-45% |





