CNC Machining Parts Manufacturer In China
- Tight tolerances | Complex geometries | Reliable results
- Rapid prototyping and scalable production
- Transparent pricing and responsive communication
- Quality you can trust | Delivery you can depend on
Your 24/7 Quote Service
Our CNC Machining Capabilities
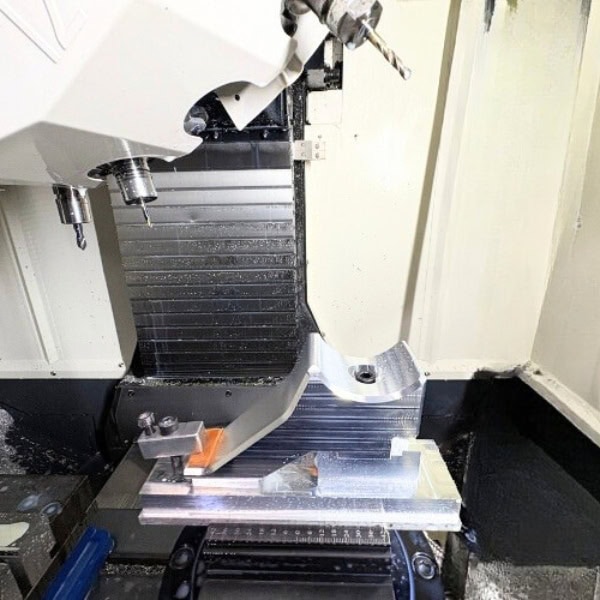
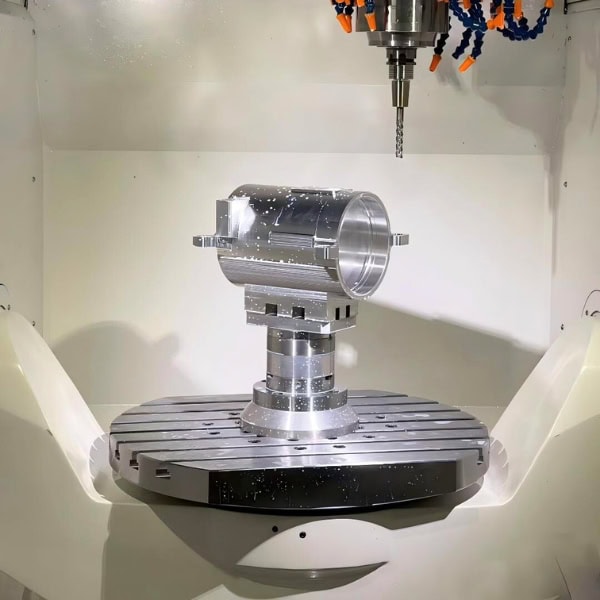
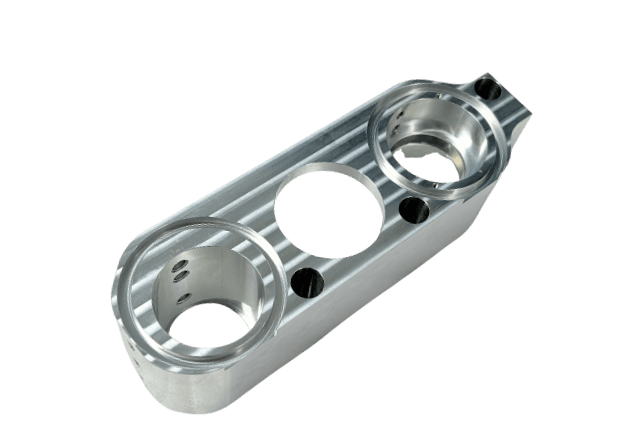
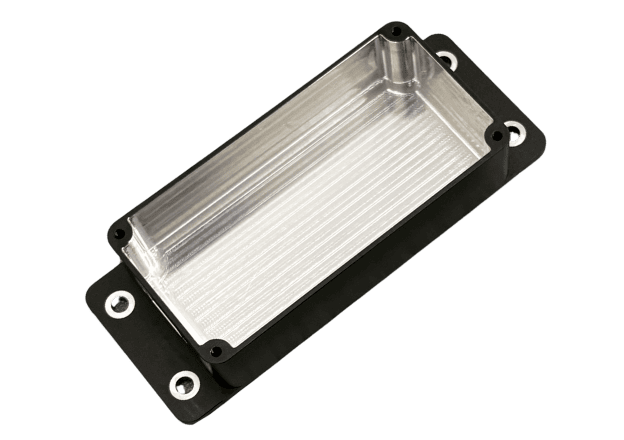
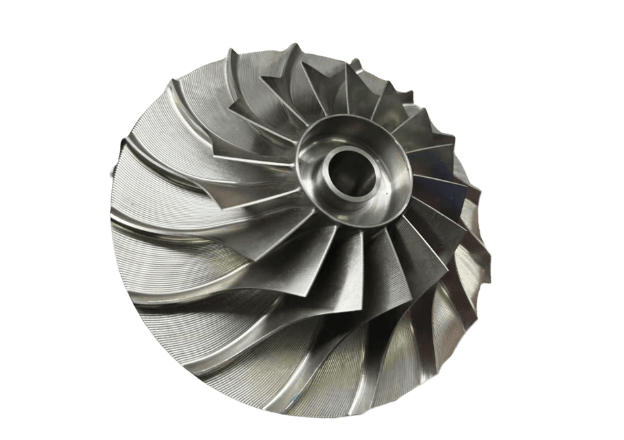
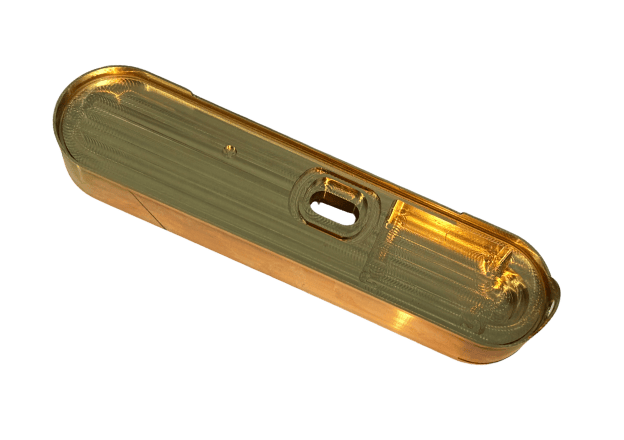
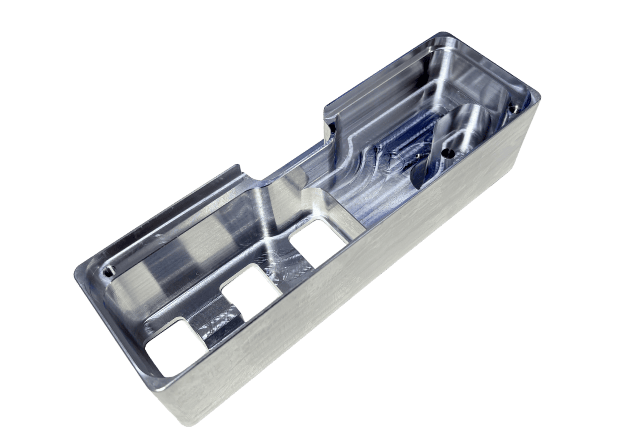
Custom Metal CNC Machining Parts



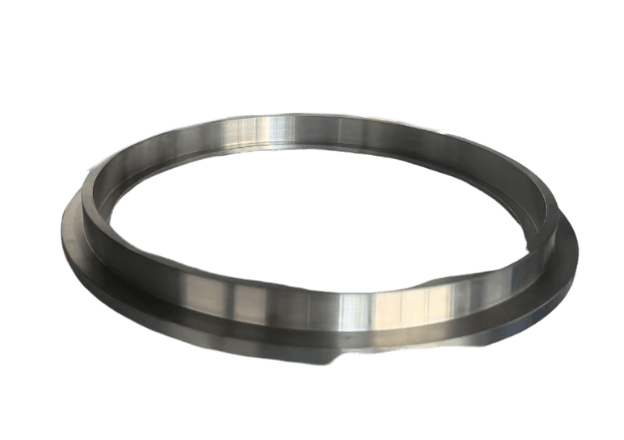
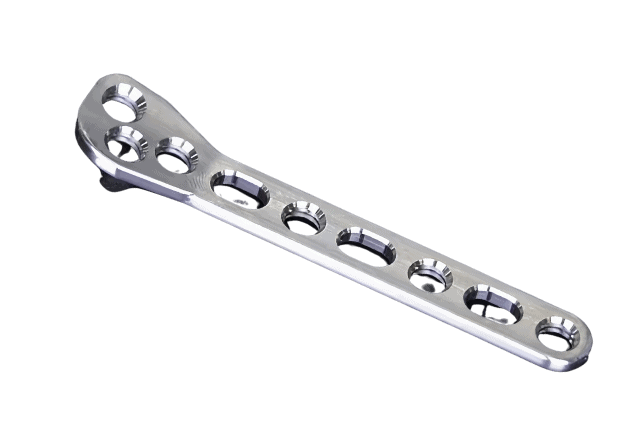

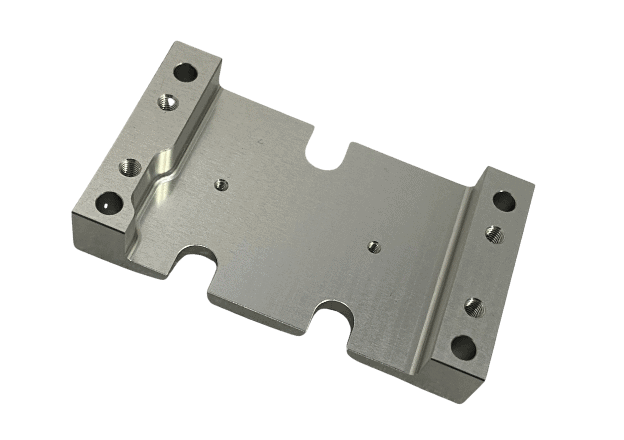
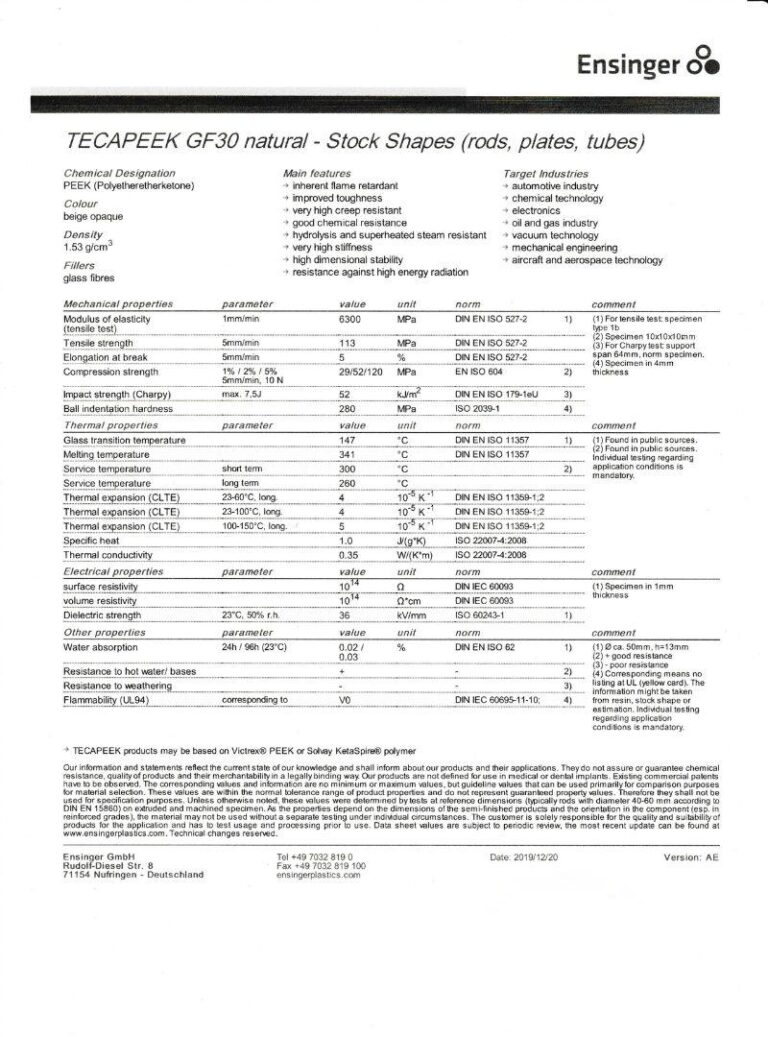
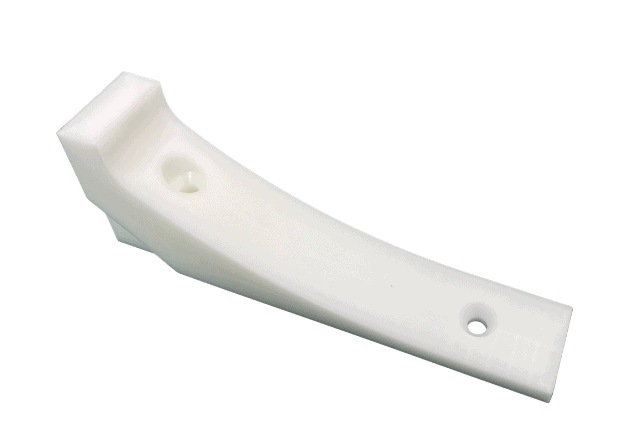
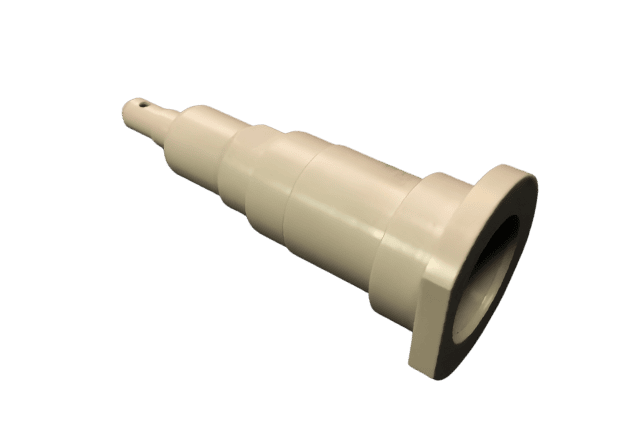
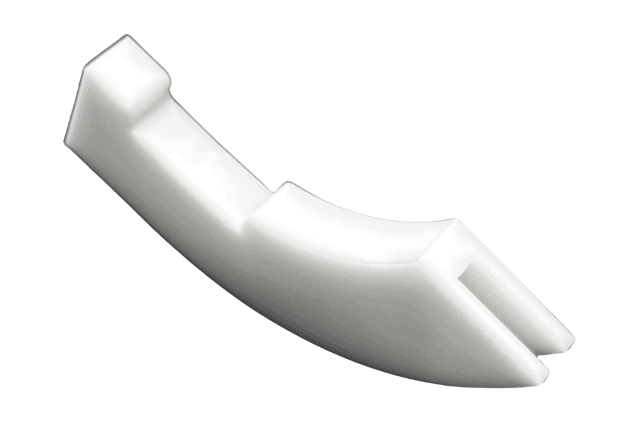
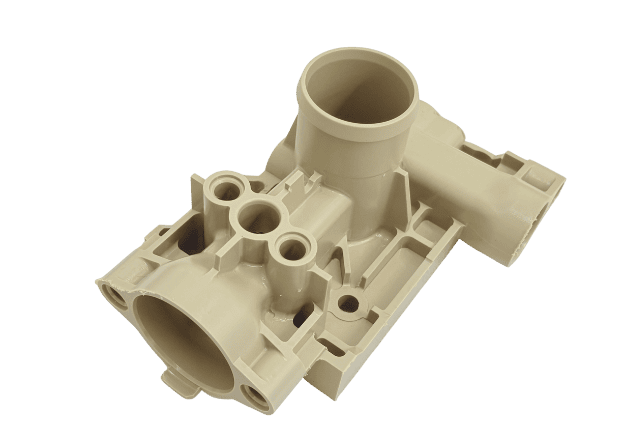
Custom CNC Plastic Machining Parts
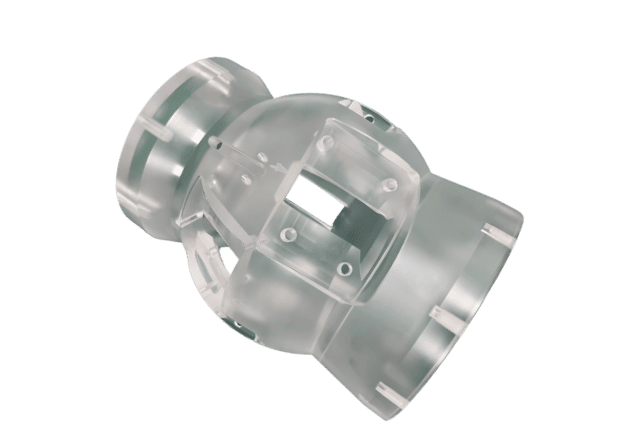
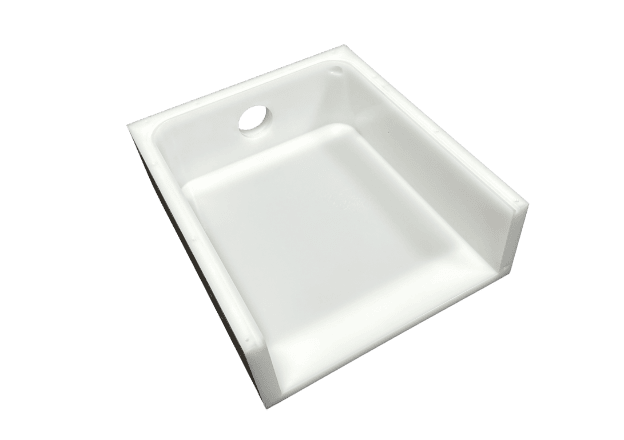
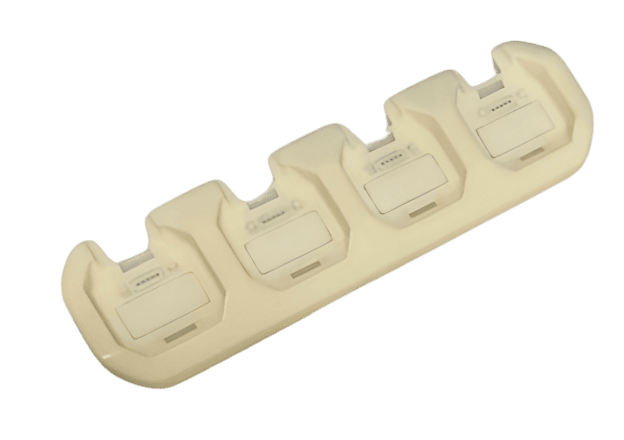




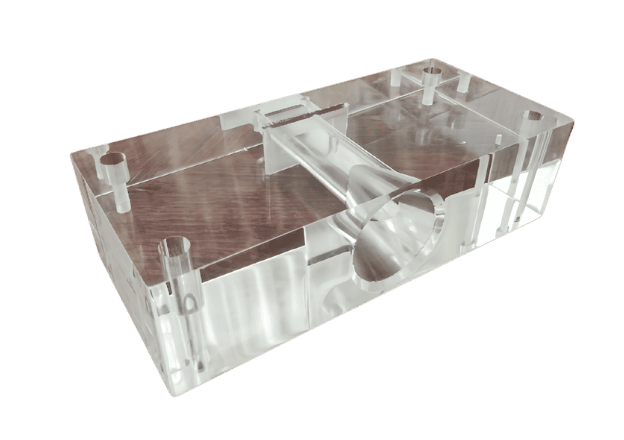


About TiRapid
TiRapid is a trusted CNC machining parts supplier and manufacturing company based in Zhongshan, China, near Shenzhen. Since 2010, we have helped global customers solve complex machining challenges with precision, speed, and reliability.
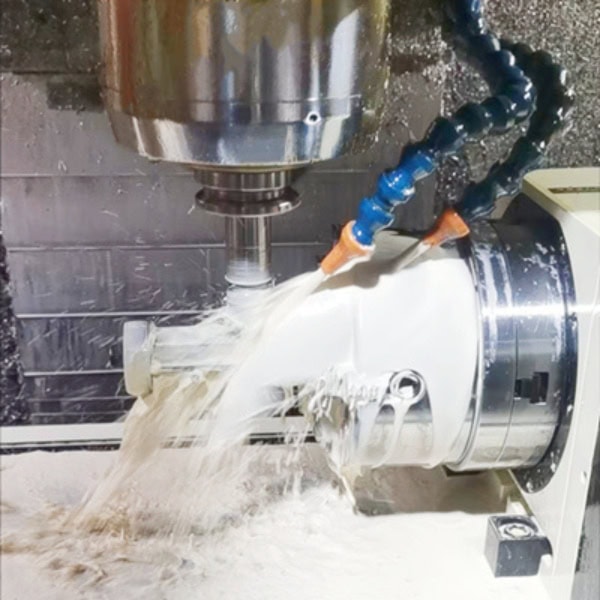
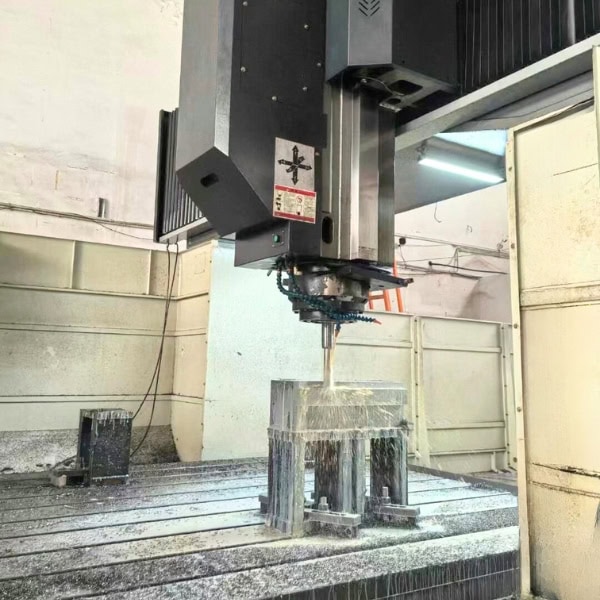
Equipped with advanced 3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis, and large-part machining capabilities, we provide flexible CNC machining services for prototypes, low-volume production, and high-precision components. From material selection to manufacturability optimization, our engineering team works closely with you to reduce risk, control cost, and improve performance.
We are committed to delivering dependable service and consistent quality—so you can move your project forward with confidence.

Why Choose TiRapid

Reliable Precision for Tight Tolerances
Engineering Support That Reduces Risk

Flexible Production From Prototype to Volume
Transparent Communication and Global Service
Fast Lead Times And Compromising Quality
FAQs
How can I pay you as an individual? What are the payment terms?
It’s convenient for your payment. We have EURO and USD company account, and paypal personal account.
How quickly can you deliver the machined parts?
Standard orders are completed within 7-10 days, while urgent orders can be prioritized and delivered within 3-5 days. Our flexible production schedule ensures that you receive high-quality parts without delaying your project timeline. If you’re working on a tight deadline, feel free to contact our team, and we’ll provide the fastest delivery plan.
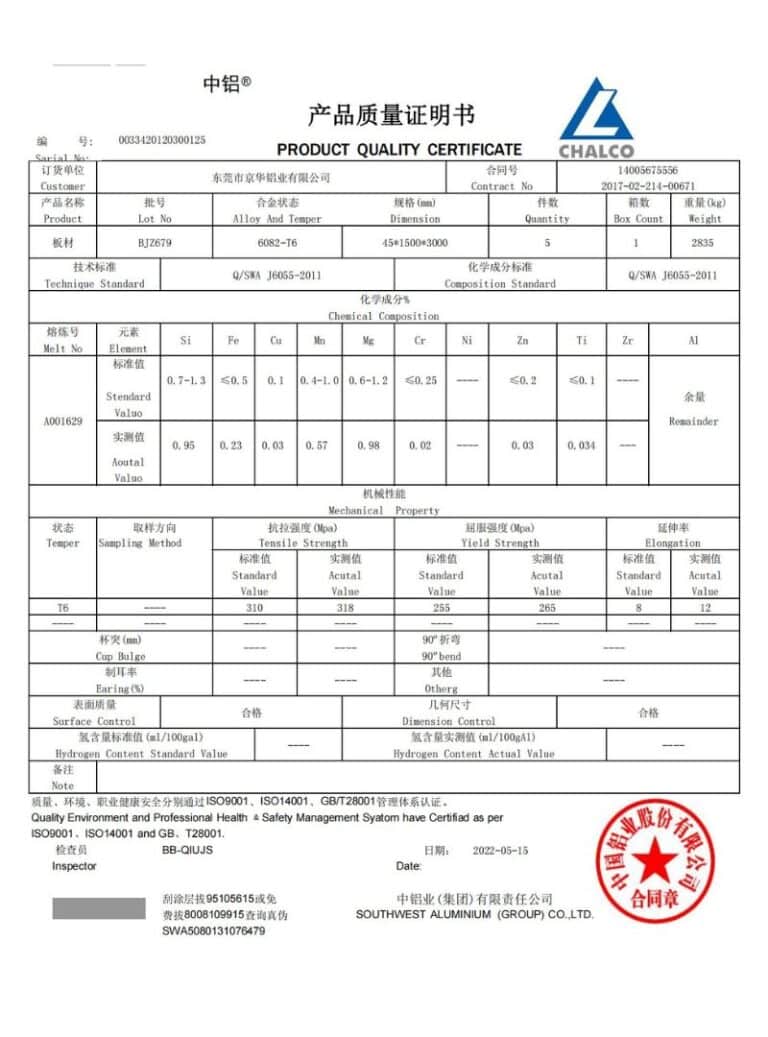
How does TiRapid ensure product quality?
We follow a strict three-stage quality inspection process:
- Material Inspection: All raw materials are thoroughly checked before entering production to ensure they meet project requirements.
- In-Process Inspection: Operators and inspectors monitor every production step in real-time.
- Final Inspection: Before delivery, we perform comprehensive quality checks using advanced equipment, such as CMM and projectors, to ensure all parts meet your specifications.
Additionally, our quality management system is ISO 9001:2015 certified, providing you with complete peace of mind.
Can you handle small batch orders?
Of course! We have no minimum order quantity requirements. Whether you need a single prototype, 10 pieces for a small batch, or thousands for mass production, we can handle your needs with flexibility. For small batch orders, we also offer quick-turnaround services to help you validate designs and move your project forward faster.
What are your shipping services?
We rely on top-tier couriers such as UPS, FedEx, and DHL to ensure timely, safe, and reliable delivery of parts to our customers.
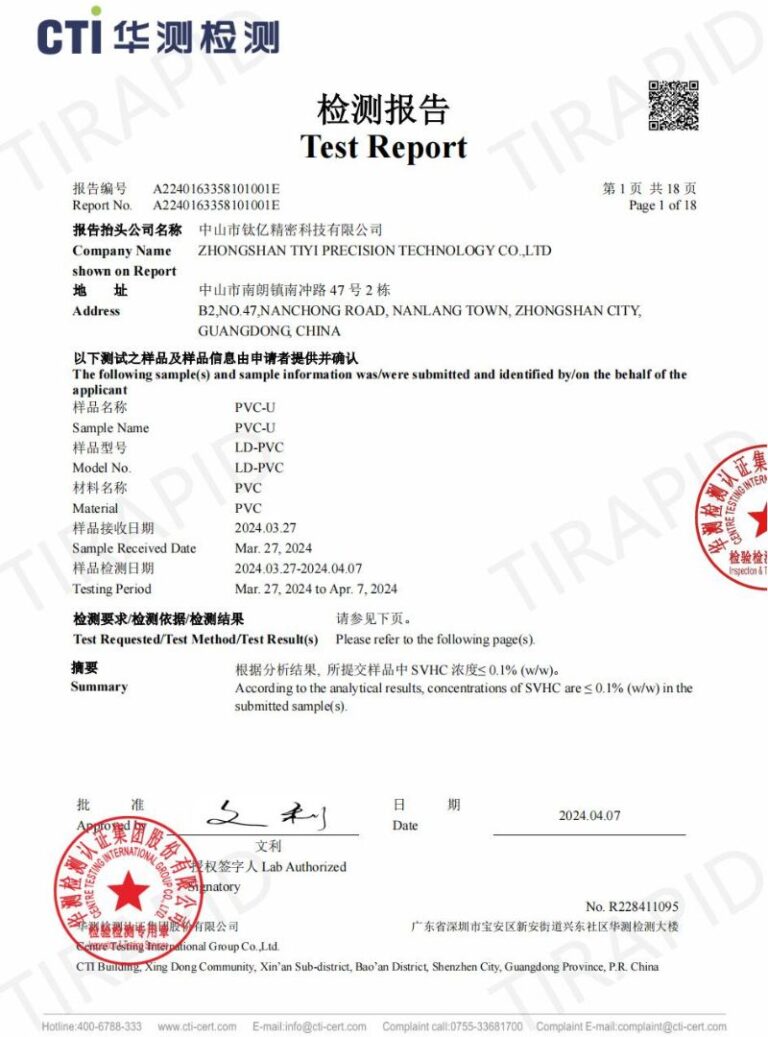
Do you have any certification?
Yes, our products can pass ISO9001, ROHS & REACH certification.