ABS is one of the indispensable engineering materials in manufacturing. As a durable and economical thermoplastic polymer, ABS plays an important role in many key industries, from automobiles to appliances, from consumer electronics to building materials. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the basic properties of ABS, production methods, processing technologies and its applications in different fields.
What is ABS Plastic
ABS plastic is produced through chemical synthesis and is not derived directly from natural resources. It is produced by the polymerization of three chemicals: acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene. These chemicals are usually prepared through complex chemical reactions during petroleum refining and chemical processes.ABS is usually presented in three shapes: plate, rod, and pellet.
Typical Mechanical Properties of ABS Material
Advantages
- High toughness: It has good impact resistance, lower temperature (-20℃) can also maintain a certain degree of toughness.
- Easy to process: It is easy to process and mold, suitable for: CNC machining, injection molding, extrusion, welding.
- Smooth surface: It parts have a smooth surface that is easy to print and paint.
- Cost Effective: It is less expensive than many other engineering plastics.
Disadvantages
- Poor temperature resistance: ABS cannot be used in high-temperature environments. The melting range of ABS is approximately 190°C to 270°C (374°F to 518°F), and prolonged exposure to high temperatures can result in distortion or yellowing of the material.
- Poor chemical resistance: ABS is sensitive to strong acids, alkalis and certain organic solvents and is not suitable for use in these specific environments.
Types and Grades of ABS Plastic
1. General Purpose ABS
- This is the most common type of ABS and is used in a variety of general industry applications such as appliance housings, toys, and some non-load bearing parts.
- Good mechanical and processing properties for most standard injection and extrusion molding processes.
2. Highly Mobile ABS
- Especially designed for injection molding of complex, thin-walled products with higher fluidity.
- Material can flow faster in the mold and fill fine and complex geometries.
3. High Impact ABS
- The impact strength of ABS has been improved through a modified formulation for applications requiring higher toughness and impact resistance.
- Commonly used for safety-related parts and products for outdoor use.
4. Highly Heat-Resistant ABS
- Modification of standard ABS improves the heat resistance of the material, which can withstand higher operating temperatures.
- Ideal for automotive interiors, electronic equipment and other applications that may be exposed to higher temperature environments.
5. Transparent ABS
- Provides better transparency for products that require a transparent window or appearance, such as appliance panels and toys.
- The material is usually not completely transparent, and its transparency can be dramatically improved with specific additives and formulations.

6. Flame Retardant ABS
- ABS with added flame retardants for applications that require compliance with specific flame retardant standards, such as electronic and electrical components.
- It slows the spread of flames and reduces the risk of fire.
7. Enhanced ABS
- Glass fiber reinforced or carbon fiber reinforced ABS provides higher mechanical strength and rigidity.
- Typically used in engineering applications where extra strength and rigidity is required.
8. Renewable or Bio-Based ABS
- New ABS materials under development, made from partially bio-based or recycled materials to improve environmental sustainability.
- Reduces dependence on traditional chemical and petroleum fuels and provides similar performance to traditional ABS.
How to Produce ABS Plastic
ABS plastics are produced mainly by emulsion polymerization, suspension polymerization or continuous mass polymerization methods. Each production process has its own characteristics:
- Emulsion polymerization: is one of the most common methods of producing ABS and involves the polymerization of monomers in an aqueous phase. This method produces ABS particles with a very fine structure and is suitable for applications requiring a high surface finish.
- Suspension polymerization: is the suspension and polymerization of monomers in water in the form of small droplets. This method produces larger ABS particles than emulsion polymerization and is typically used for applications requiring larger particles.
- Continuous mass polymerization: a highly efficient production method that allows for continuous production of ABS and increased production efficiency. It is suitable for mass production and can effectively control the physical and chemical properties of the product.
Different Processing Technologies for ABS Material
ABS plastics can be processed in a variety of ways, selected according to product function and tolerance requirements:
1. CNC Machining of ABS Plastic
CNC machining is a machining technology that cuts material by means of a tool (subtractive machining), mainly including CNC milling and CNC turning, which cuts, drills, and mills plates or bars, and is suitable for manufacturing complex or small-lot parts.
Key tips for CNC machining:
Tip 1: Cutter (tool) selection: Select cutting tools suitable for ABS plastic and use aluminum cutting tools.
Tip 2: Cutting parameter setting: Appropriately reduce the spindle speed to prevent the material from melting and reduce internal stress.
Tip 3: Cooling and Lubrication: Choose environmentally friendly grade coolant to avoid contamination of the material by the coolant.
Tip 4: Control deformation: ABS material deforms during machining due to cutting forces or heat, so it is necessary to ensure that the workpiece is fixed and stable to minimize cutting forces.
Tip 5:Cleaning the workpiece: after processing is completed, clean the product in time. Avoid the coolant being adsorbed by the material.
Tip 6 :INSPECTION AND QUALITY CONTROL: Parts should be inspected for size and appearance during and after machining to ensure that product specifications are met. Regular calibration of inspection tools to ensure accurate inspection results.
2. ABS Rapid Tools
Rapid tooling is made of P20 tool steel, enables the rapid production of molds for injection molding in a short period of time (within 10 days) in order to obtain functional parts or prototypes quickly, preferable to traditional mold making.
Key tips for rapid tool manufacturing:
Tip 1: Material Handling
- Ensure that the material is thoroughly dry to avoid bubbles or defects caused by high moisture content during processing.
Tip 2: Mold Design and Manufacturing Quality
- Accurate mold design is the key to ensure product quality. Use of high quality mold materials and regular maintenance of the mold.
Tip 3: Quality Control
- Establish a strict quality testing process, conduct sampling for each batch of products and keep inspection records.
- Analyze the causes of quality problems that occur, make timely improvements, and quickly adjust the manufacturing process to avoid repetition.
3. Injection Molding
The injection molding process begins by heating ABS pellets to a molten state and then injecting them into a mold using the screw of an injection molding machine. Inside the mold, the plastic cools and solidifies, eventually forming the desired product shape.
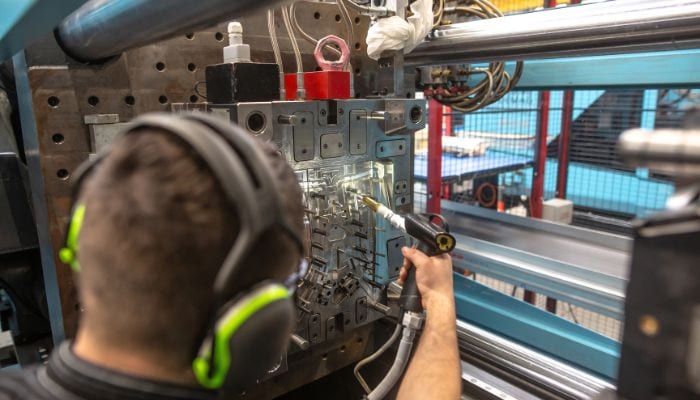

Tips for injection molding manufacturing:
Tip 1: Material Preparation.
- Ensure that the ABS pellets are sufficiently dry to avoid bubbles, silvering or degradation due to excessive moisture during the injection molding process.
- If colors or additives are used, it is necessary to ensure that these additives are well mixed with the ABS particles.
Tip 2: Machine Settings
- Temperature Control: Precise control of the temperature of the heated barrel and mold. Improper temperature settings may result in material decomposition or incomplete melting, affecting product quality.
- Pressure and Speed Adjustment: Set the injection pressure and speed correctly to ensure that the ABS melt fills the mold adequately and uniformly to avoid short shots or flashing edges.
Tip 3: Mold Design and Maintenance
- Mold Quality: Use high quality molds to ensure precision and durability of the molds. The design of the molds should take into account good gas emission and cooling channel layout.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly check and maintain the molds, keep the molds clean, repair the damaged or worn parts in time to avoid product defects caused by mold problems.
Tip 4: Production Monitoring
- Real-time monitoring: real-time monitoring of the production process through on-site monitoring or the use of sensor technology, timely adjustment of parameters to solve production problems.
- Quality Inspection: Establish a strict quality control system and conduct regular and random inspections of the parts produced to ensure that each batch of products meets the quality standards.
Tip 5: Operator Training
- Regular training: Regular training is provided to operators on machine operation, maintenance and troubleshooting to ensure that they are able to operate the equipment correctly and solve production problems.
Tip 6: Cost Control
- Optimize production processes: Reduce material waste and cycle time through process optimization, such as using multi-cavity molds or rationalizing production schedules.
- Material and energy use: Optimize material use and energy consumption, select cost-effective raw material suppliers and improve energy efficiency.
4. ABS Extrusion Molding
ABS extrusion molding is the process of extruding ABS material through a specific shaped die of a high temperature extruder. This technology is widely used to produce continuous shaped plastic products such as pipes, profiles, sheets and films.

Key tips for ABS extrusion molding:
Tip 1: Material Preparation
- Drying: Ensure that the ABS pellets are thoroughly dried; ABS is highly absorbent and if processed without drying, air bubbles will form in the product, affecting its appearance and performance.
- Homogeneous mixing: Add color or other additives, should ensure that these substances and ABS particles are fully mixed evenly to ensure the consistency of product color and performance.
Tip 2: Device Settings
- Temperature control: Precisely control the temperature of the extruder’s heating zone.ABS is typically processed at higher temperatures (approximately 210°C to 270°C), and improperly set temperatures can lead to material degradation or inefficient extrusion.
- Screw speed: Adjust the rotational speed of the extruder screw to control the extrusion rate, too fast may lead to uneven material or reduced mechanical strength, too slow will reduce production efficiency.
Tip 3: Mold Design and Maintenance
- Die design: A well-designed die ensures that the shape of the extrudate is precise, and the design of the flow channel and cooling system will directly affect the quality of the product.
- Mold Maintenance: Keep the mold clean, check and maintain the mold regularly to prevent wear and clogging and avoid affecting the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the products.
Tip 4: Cooling and Towing
- Uniform Cooling: Ensure that the product can be cooled uniformly after it comes out of the mold to avoid warping or internal stress caused by uneven cooling.
- Haul-off speed: The speed of the haul-off device must be matched to the extrusion speed. Uneven haul-off will result in inconsistent product dimensions.
Tip 5: Production Process Monitoring:
- Online monitoring: real-time monitoring of key parameters in the extrusion process, such as temperature, pressure, extrusion speed, etc., allows timely adjustment of production conditions to ensure product quality.
- Regular inspection: Regular quality inspection of produced ABS products, including dimensional accuracy, physical properties and appearance inspection.
5. 3D Printing
3D printing ABS is the use of the engineering plastic ABS as a material that is printed in three dimensions on a 3D printer by means of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology. In the FDM process, the material is supplied in filament form, extruded by heating to a temperature above the melting point, and deposited layer by layer to build the 3D model.
Tips for 3D printing ABS plastic:
Tip 1: Drying of materials
- ABS has a certain degree of hygroscopicity. Excessive humidity will produce vapors during the printing process, affecting the print quality. Therefore, you should ensure that the ABS filament is dry before use, and you can pre-treat the material with a drying oven.
Tip 2: Print Temperature Control
- ABS is generally printed at temperatures between 220°C and 250° Too low a temperature and the material will not melt sufficiently, resulting in poor adhesion between the printed layers; too high a temperature may result in scorching of the material or loss of strength.
- The print bed temperature is also critical and usually needs to be between 90°C and 110°C to ensure good adhesion of the substrate.
Tip 3: Print Speed
- The printing speed of ABS material should not be too fast, too fast may lead to poor bonding between the printed layers, affecting the structural strength of the finished product.
Tip 4: Printing Environment
- ABS is prone to warping when cooled, so it is best to do this in a closed printing environment to keep the ambient temperature stable.
Tip 5: Post-processing
- The support structure after ABS printing needs to be removed carefully so as not to damage the main model.
- Prints may require subsequent operations such as sanding, drilling or painting to achieve a higher surface finish and aesthetics.
Tip 6: Health and safety:
- Printing ABS releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as styrene, which may be detrimental to your health when exposed for long periods of time. Ensure that the printing area is well ventilated and use appropriate respiratory protection if necessary.
6. Welding ABS
Welding ABS is achieved by joining two parts together by the principle of heat fusion, using a variety of welding techniques.Welding of ABS is commonly done by hot air, extrusion, hot plate or ultrasonic welding techniques.
How to improve ABS welding quality:
Tip 1: Surface Preparation Before Welding: Clean the welding surface to ensure that it is free of oil, dust or other contaminants.
Tip 2: Selecting the right welding method
- Hot Gas Welding: Suitable for small to medium sized parts. Carried out using a hot gas torch and ABS welding rods.
- Extrusion welding: for larger parts or seams that require higher strength.
- Ultrasonic welding: For small or ABS parts that require high precision.
- Hot plate welding: for large and heavy plastic parts.
Tip 3: Optimization of welding parameters: Adjust the temperature, pressure and time parameters according to the chosen welding method.
Tip 4: Use the proper welding speed: Match the welding speed to the material melting rate to avoid underfusing or overheating the weld.
Tip 5: Post-treatment and inspection: Allow sufficient cooling time after welding to prevent stress cracking of the weld.
Tip 6: Environmental control: Welding is performed in stable environmental conditions, avoiding temperature fluctuations and excessive humidity.

Application of ABS Material
- Automobile industry: ABS material occupies an important position in the automobile industry, and can be used to manufacture various parts of automobiles, such as hubcaps, lampshades, protective covers and so on.
- Electronic and electrical appliances industry: In the electronic and electrical appliances industry, ABS materials also play an important role. It is used to manufacture the shells of electronic products such as televisions and computers.
- Household appliance industry: ABS materials are widely used in the household appliance industry, such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, etc. The control panels, door panels and other parts of the appliances are made of ABS plastic.
- Construction and Decoration Industry: ABS plastics are used in the construction and decoration industry, such as doors, windows, partitions, decorative panels and other building materials manufacturing.
FAQs
What is the temperature range of ABS material?
ABS plastic is typically used at temperatures between -20°C and 80°C, and can withstand temperatures up to 100°C for short periods of time. This makes ABS thermally stable for everyday applications, but unsuitable for prolonged exposure to higher temperatures.
Is ABS recyclable?
ABS plastic can be reused through mechanical recycling. The recycling process usually includes crushing, washing, drying and re-pelletizing. Since it can produce hazardous substances during processing, the recycling process needs to be properly managed to minimize the impact on the environment and human health.
Is ABS harmful?
This material is safe and harmless under normal use conditions. When high temperatures (over 250°C) are reached during certain processes, harmful gases such as styrene and acrylonitrile may be released.
Conclusion
ABS plastics occupy an important position in the field of engineering plastics due to their unique material composition and wide range of application properties. Their well-balanced mechanical properties and good processing characteristics excel in demanding applications. Whether for durability, aesthetics or functionality, ABS plastics offer efficient solutions.
If you are looking for high quality ABS products at competitive prices, Tirapid is the right choice for you, as we have extensive experience in ABS processing. Feel free to contact our mechanical engineers.