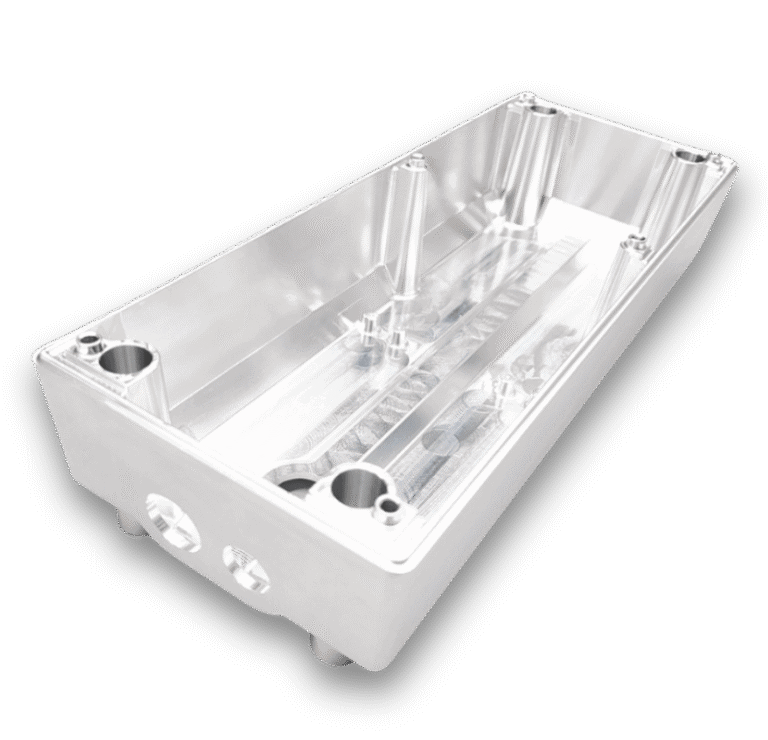
CNC Machining Services for Custom Parts
TiRapid offers flexible CNC machining services for both metal and plastic parts. From custom one-off pieces to high-volume production, we ensure delivery in as fast as 1 day, giving your production plan a competitive edge.



- Free Design
- No MOQ Required
- Competitive Pricing
- Large Part Machining (up to 118″)
Your 24 hour quote
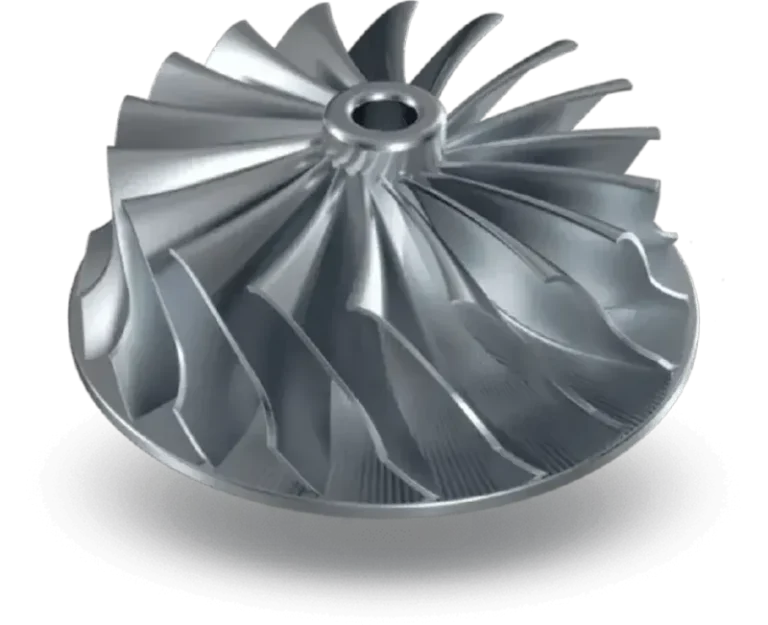

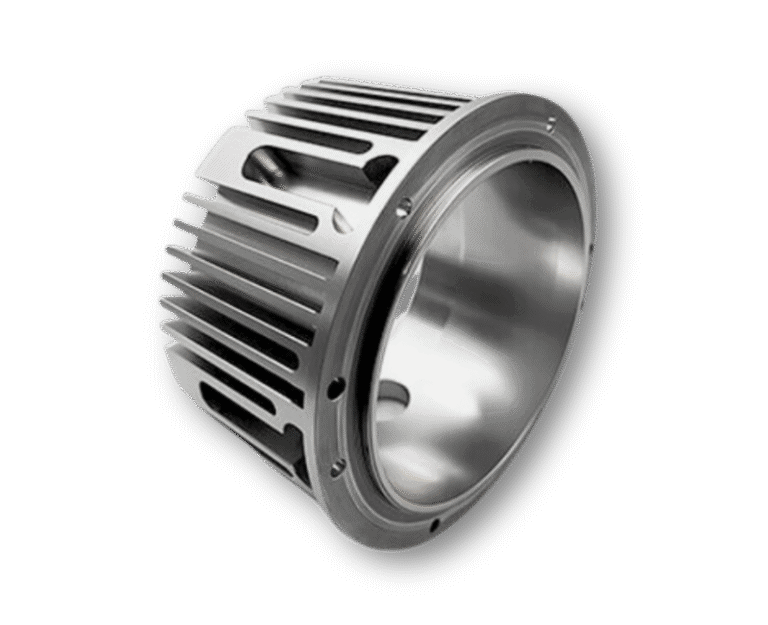
Our Manufacturing Capabilities

3 & 5 Axis CNC Milling
5-axis machining can precisely process complex surfaces, multi-faceted and angled features, reducing machining time.
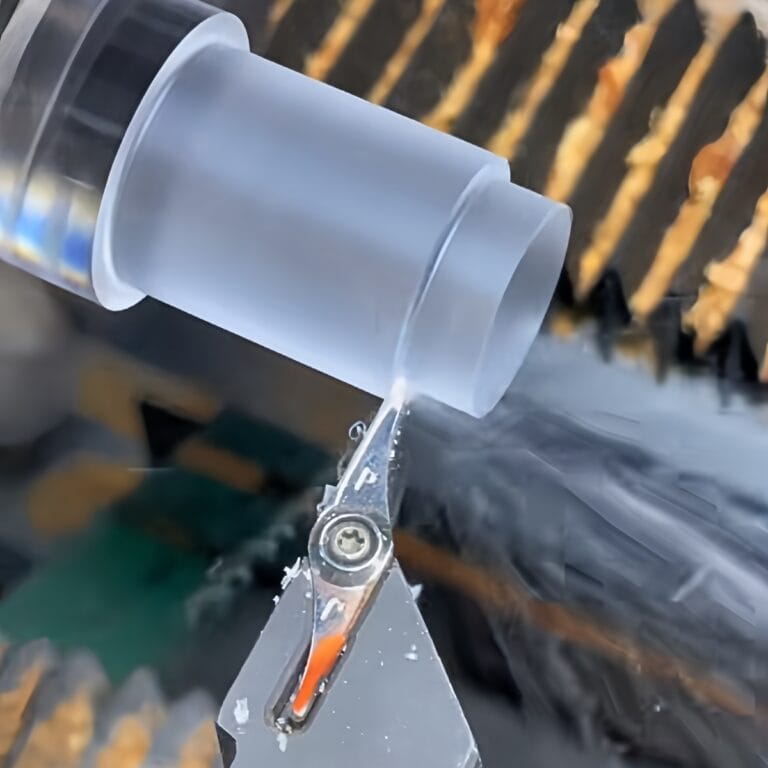

CNC Turning
CNC turning can accurately produce circular and cylindrical parts, providing high-quality surface finishes.

EDM
EDM can machine high-hardness materials, sharp corners, right angles, and complex contours.

Wire EDM
Wire EDM is capable of cutting deep holes and producing high-precision, fine contours in parts.
Materials We Work With
CNC machining is suitable for processing a variety of materials, can stably achieve high-quality production, and is suitable for batch processing of different materials such as metals, plastics, and composite materials. We have more than 40+ kinds of materials that can be processed, the following is just a small list of materials.

Metals
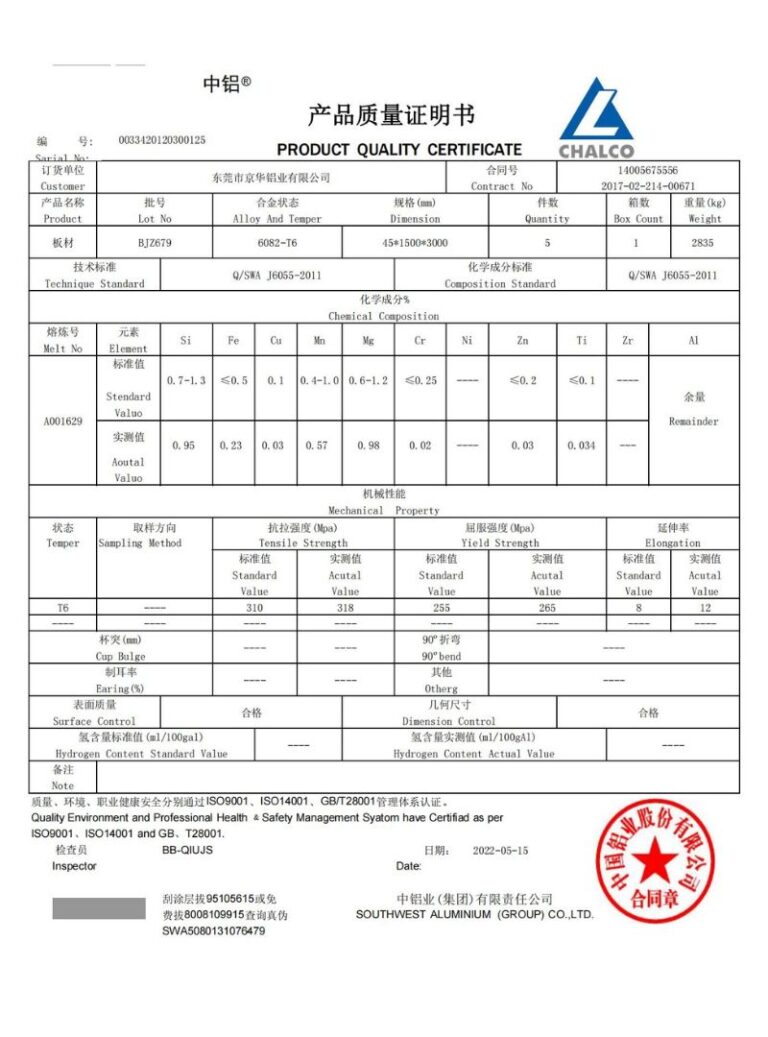
- Aluminum 6061/7075/6082
- Stainless Steel 304/316
- Steel 1018/4140/A3/A2
- Brass C36000/C28000
- Copper C11000
- Titanium Grade5/Grade1

Plastics
- POM
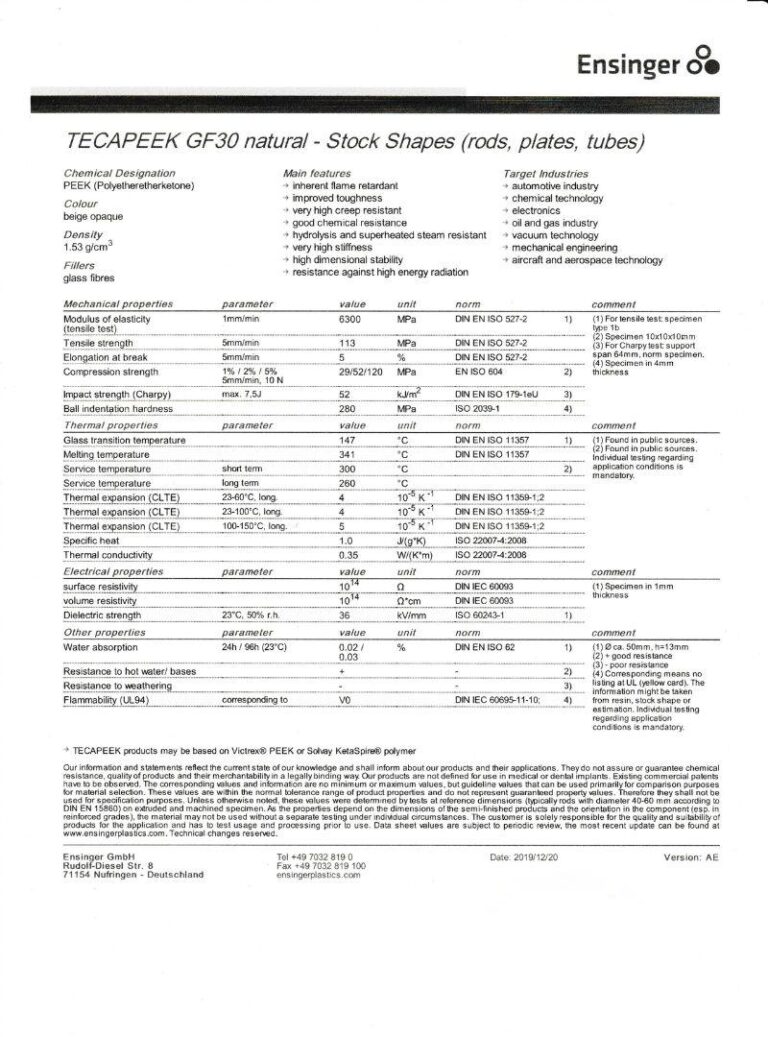
- PEEK
- PVC
- PTFE / ABS
- ABS / PC
- PP / PEI (ULTEM 1000)

Composites
- CFRP
- AFRP
- BFRP
- MMC
- PMC
- GFRP
Why Choose TiRapid

Secure & Confidential Manufacturing
Full-Spectrum Manufacturing Capabilities
Fast Turnaround & On-Time Delivery

No Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Multi-Material Manufacturing Options
Design & Process Optimization
Our Project Team
We are a knowledgeable, lean and experienced team of engineers. To contact us,
please see the contact details below and one of our team members will be happy to assist you.

Bella Liang

Galen Cui

Maggie Du

Nick Zhai

Rea Tang

Zoey Yong

Kaya Chen

Lin Fu

Candy Liu

Chloe Xu
Trusted by 3,00+ Companies for Manufacturer

Aerospace & aviation
Medical Equipments

Aerospace & aviation

Robotics & Automations
TiRapid's track record






What Our Customers Say





Frequently Asked Questions
How can I pay you as an individual? What are the payment terms?
It’s convenient for your payment. We have EURO and USD company account, and paypal personal account(+4% handling fee).
How fast can you deliver parts?
TIRAPID is known for its quick response times. Standard orders are completed within 7-10 days, while urgent orders can be prioritized and delivered within 3-5 days. Our flexible production schedule ensures that you receive high-quality parts without delaying your project timeline. If you’re working on a tight deadline, feel free to contact our team, and we’ll provide the fastest delivery plan.
How does TiRapid ensure product quality?
We follow a strict three-stage quality inspection process:
- Material Inspection: All raw materials are thoroughly checked before entering production to ensure they meet project requirements.
- In-Process Inspection: Operators and inspectors monitor every production step in real-time.
- Final Inspection: Before delivery, we perform comprehensive quality checks using advanced equipment, such as CMM and projectors, to ensure all parts meet your specifications.
Additionally, our quality management system is ISO 9001:2015 certified, providing you with complete peace of mind.
Can you handle small batch orders?
Of course! We have no minimum order quantity requirements. Whether you need a single prototype, 10 pieces for a small batch, or thousands for mass production, we can handle your needs with flexibility. For small batch orders, we also offer quick-turnaround services to help you validate designs and move your project forward faster.
What are your shipping services?
We rely on top-tier couriers such as UPS, FedEx, and DHL to ensure timely, safe, and reliable delivery of parts to our customers.
Do you have any certification?
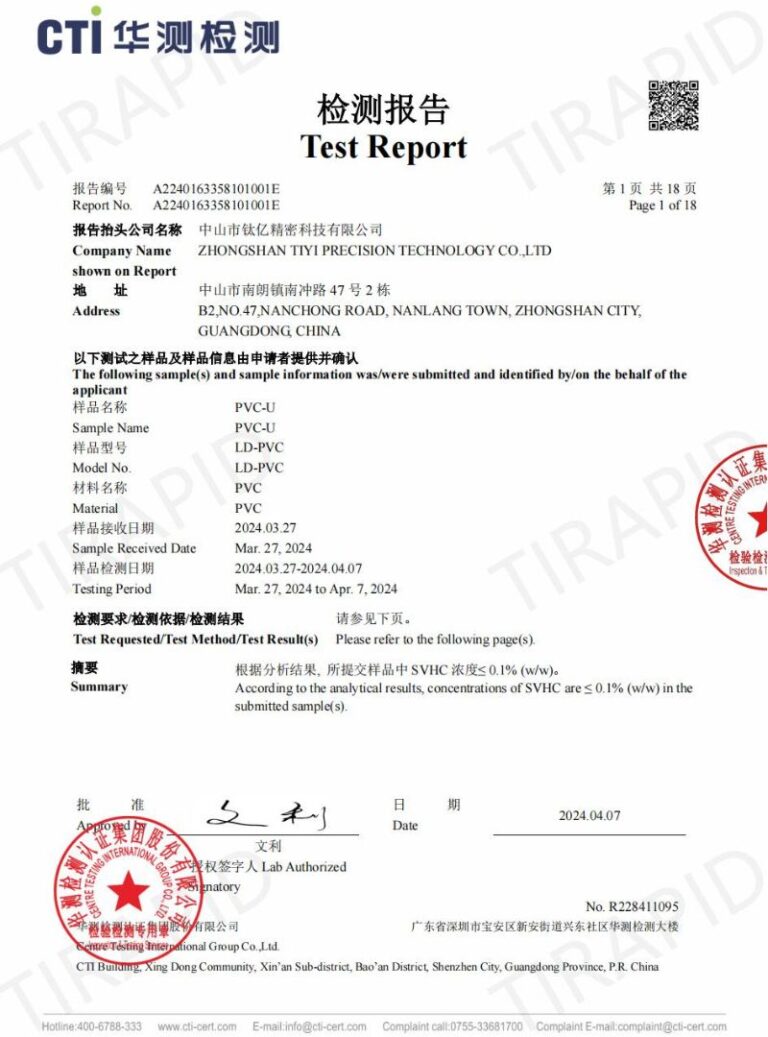
Yes, our products can pass ISO9001, ROHS & REACH certification.