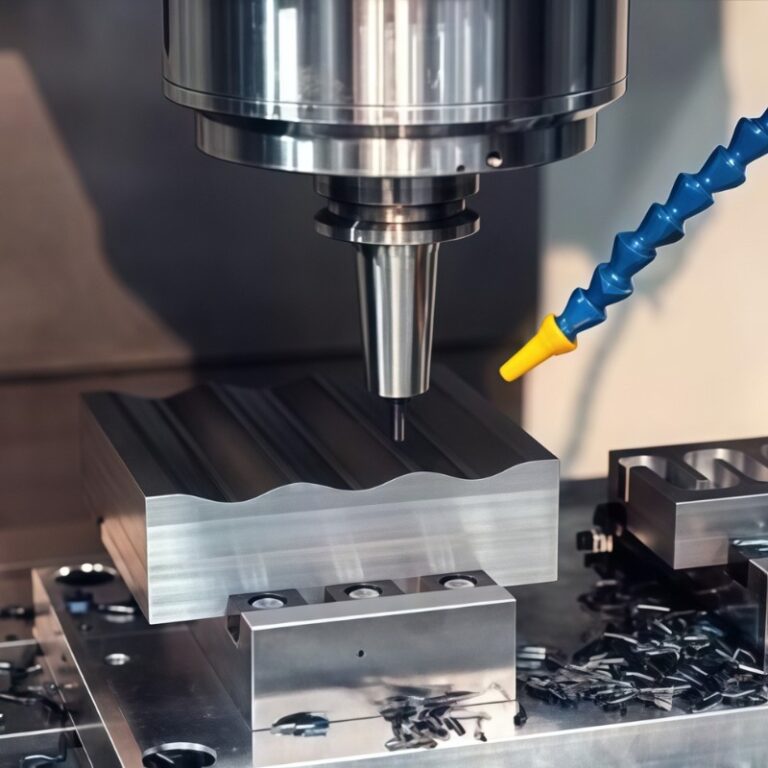
Are you developing a new product or part but unsure where to start production? A CNC machine shop is the bridge between design and manufacturing—where raw materials are transformed into precision parts using computer-controlled equipment. This guide explains how CNC shops work, their advantages, and how to choose the right one for your project.
What Is A CNC Machine Shop
A CNC machine shop is a modern manufacturing facility where raw materials—typically metals or plastics—are transformed into precision components through computer-controlled machining. Unlike traditional manual workshops, CNC shops integrate advanced technologies such as 3-, 4-, and 5-axis milling, turning, EDM, and CMM inspection to achieve micron-level accuracy.
Get 20% offf
Your First Order
At its core, a CNC machine shop specializes in subtractive manufacturing—removing material from a solid block to form complex geometries that meet exact design specifications. These shops are the backbone of industries like aerospace, automotive, robotics, and medical devices, where precision and consistency are vital.
For example, TiRapid’s CNC facility produces custom prototypes and small-batch parts for European robotics companies. By combining CAD/CAM automation, high-speed machining centers, and rigorous quality control, we achieve tolerances up to ±0.01 mm. Whether it’s a single prototype or 10,000-piece production run, a professional CNC machine shop ensures efficiency, repeatability, and quality every step of the way.
What Do CNC Machine Shops Do
CNC machine shops are precision manufacturing facilities that transform raw materials into functional parts using automated,computer-controlled tools. Every operation—from cutting and drilling to polishing and inspection—is designed to ensure accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency.
1. Core CNC Machining Operations
CNC Milling – Uses rotating cutters to remove material from a stationary block, ideal for complex 3D surfaces and cavities.
CNC Turning – Rotates the workpiece while a fixed tool cuts cylindrical shapes, perfect for shafts, bushings, and round parts.
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) – Removes material using electrical sparks, ideal for hard alloys and intricate shapes.
Grinding – Achieves ultra-smooth finishes and tight flatness tolerances on metal surfaces.
2. Auxiliary Manufacturing Processes
Drilling & Tapping – Adds threaded holes or mounting features.
Sawing & Cutting – Prepares material blanks before precision machining.
Deburring & Cleaning – Removes burrs and residues after cutting for smoother assembly.
3. Surface Finishing Capabilities
Anodizing, Bead Blasting, Powder Coating – Enhance corrosion resistance, wear life, and appearance.
Polishing & Brushing – Achieve mirror-like or satin textures for aesthetic or functional purposes.
4. Inspection & Quality Control
CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) – Measures part geometry with micron-level accuracy.
Optical and Surface Roughness Testing – Ensures every dimension meets design intent.
ISO9001 Processes – Standardized workflow to maintain global quality standards.
5. Integration and Digital Workflow
Modern CNC machine shops use CAD/CAM software to translate 3D models into machine code (G-code). This ensures seamless coordination between design, production, and inspection.
For example, at TiRapid, our engineers use advanced 5-axis machining centers with automated inspection systems to achieve ±0.01 mm precision. Whether for a prototype or 10,000-piece batch, every part is traceable, consistent, and ready for end-use.
Digitalization & Automation
Digitalization and automation are transforming traditional CNC machine shops into smart, data-driven factories. By integrating CAD/CAM systems, AI-assisted machining, and robotic automation, manufacturers achieve faster production cycles, fewer errors, and higher consistency across large-scale operations.
1. CAD/CAM Integration
Modern CNC workflows start with digital design. CAD/CAM software automatically converts 3D models into machining code (G-code), ensuring precise toolpaths and minimizing manual setup time.
At TiRapid, every project is simulated digitally before machining begins, guaranteeing first-pass success and zero rework.
2. Smart Machining Systems
AI and IoT-enabled CNC machines monitor tool wear, cutting speed, and vibration in real time. Predictive maintenance prevents downtime, while digital twins allow engineers to adjust parameters virtually before production.
3. Robotic Automation
Automated loading, tool changing, and material handling reduce labor dependence and increase productivity. Collaborative robots (cobots) now handle repetitive or hazardous operations with consistent accuracy.
4. Data Analytics & Traceability
Digital systems record every machining parameter, creating a transparent production history. This enhances quality control and traceability—key for aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
With full digitalization, TiRapid achieves up to 30% faster turnaround and 99.8% process accuracy, giving customers reliable and scalable manufacturing solutions.
Quality Management
Quality is the foundation of every CNC machine shop. From design verification to final inspection, every step follows international standards to ensure precision, reliability, and consistency. TiRapid’s quality management system integrates advanced testing tools and strict traceability to guarantee that every part meets exact specifications.
Standards & Certifications (ISO 9001 / AS9100 / IATF 16949)
CNC manufacturers rely on globally recognized standards to ensure product quality and customer satisfaction.
ISO 9001 – General quality management across all industries.
AS9100 – Aerospace-grade precision and documentation control.
IATF 16949 – Automotive quality management for zero-defect production.
TiRapid is certified to ISO 9001 standards and applies AS9100 and IATF principles across its production chain, ensuring full compliance for aerospace, medical, and automotive projects.
Process Control: FAI, PPAP, SPC, MSA
Every CNC process is controlled through data-driven methods:
FAI (First Article Inspection): Verifies that initial parts meet all drawing and tolerance requirements.
PPAP (Production Part Approval Process): Ensures stability and repeatability before mass production.
SPC (Statistical Process Control): Monitors real-time machining data to detect deviations.
MSA (Measurement System Analysis): Validates inspection tools for consistent accuracy.
At TiRapid, our SPC systems record cutting parameters and CMM inspection data, maintaining ±0.01 mm precision consistency across batches.
Traceability: Material, Batches, COC/ROHS/REACH
Traceability ensures that every component’s material and production record can be tracked throughout its lifecycle.
Each batch includes Material Certificates, COC (Certificate of Conformance), and Compliance with ROHS/REACH.
Full digital batch tracking links each part to raw material, process parameters, and inspection results.
This traceability builds customer confidence, especially for aerospace, automotive, and electronics projects requiring regulatory compliance
Safety Essentials
A CNC machine shop is a precision-driven environment where safety is just as critical as accuracy. Operators must follow strict rules to protect themselves and maintain efficient workflow. Adhering to proper safety protocols reduces accidents, prevents damage, and ensures continuous production without interruption.
PPE & Shop Floor Rules
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the first line of defense in any machining environment.
Always wear safety glasses or face shields to protect against flying chips.
Avoid loose clothing, jewelry, and open-toed shoes that may catch in machinery.
Use safety shoes with non-slip soles and tie back long hair.
Keep the floor clean and dry to prevent slips or falls.
Following these rules ensures every machinist operates in a safe, organized workspace where risks are minimized.
Machine Operation & Lockout/Tagout
Before operating any CNC or manual machine, workers must be fully trained and authorized.
Read and understand the operator’s manual for each piece of equipment.
Never leave running machines unattended.
Use lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance or tool changes to prevent accidental startups.
Regularly inspect machines to ensure guards, switches, and emergency stops are functioning correctly.
Strict adherence to these protocols protects personnel and prevents costly downtime due to accidents.
Material Handling & Housekeeping
Proper material handling and housekeeping are crucial for safety and productivity.
Use mechanical lifting aids or team lifts for heavy materials to prevent strain injuries.
Store raw materials and tools securely and clearly labeled to avoid tripping or falling hazards.
Keep fire-prone materials such as oil and dust away from heat sources.
Ensure emergency exits and aisles are always unobstructed and clearly marked.
A clean, well-organized shop not only improves efficiency but also promotes a safety-first culture across the workspace.
Manual vs. CNC Machining
While CNC machining has revolutionized modern manufacturing, manual machining continues to hold an important role. Both have distinct strengths, and understanding when to use each can optimize cost, speed, and precision for different production needs.

Key Comparison and Insights
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining dominates most machine shops today.
It offers unmatched precision (up to ±0.005 mm), repeatability, and automation — allowing parts to be produced 24/7 with minimal supervision. Multi-axis CNC systems can perform milling, turning, and drilling in one setup, drastically reducing human error and cycle time.
However, manual machining remains invaluable for quick turnarounds, simple parts, and one-off prototypes. Since it requires no programming, machinists can start work immediately — ideal for emergency repairs or concept validation.
Manual machines are also more affordable, with initial investments up to 80% lower than CNC equipment, making them practical for low-volume workshops and educational training.
In many advanced machine shops, manual and CNC machines coexist strategically:
CNC handles complex, high-precision production, while manual machines take care of simple or support tasks — maintaining flexibility and cost efficiency.
Summary Table: Manual vs. CNC Machining
| Feature | Manual Machining | CNC Machining |
| Programming | Not required | CAD/CAM programming needed |
| Precision | ±0.05–0.1 mm | ±0.005–0.01 mm |
| Production Volume | Low | Medium to High |
| Setup Time | Short | Longer (programming) |
| Cost | Lower equipment cost | Higher initial investment |
| Best For | Simple, one-off parts | Complex, repeatable parts |
Both methods are complementary rather than competitive — together, they ensure that every machining requirement, from rapid prototyping to mass production, can be handled efficiently.
Advantages Of Using A CNC Machine Shop
Partnering with a CNC machine shop provides companies with a powerful advantage — the ability to manufacture high-quality parts without the need for expensive equipment or in-house production lines. By outsourcing to experienced machining specialists, businesses gain access to precision, speed, and scalability across multiple industries.
High Precision And Consistency
CNC machines ensure exceptional accuracy and repeatability.
Using computer-controlled systems, cutting tools follow exact digital paths to achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm. Whether you’re producing a single prototype or 10,000 identical components, the output remains consistent.
Moreover, modern 5-axis machining allows complex geometries and smooth surface finishes that manual machining cannot easily achieve.
Production Speed And Efficiency
Automation minimizes manual input and maximizes productivity.
CNC machines can operate 24/7 under proper maintenance, reducing lead times by up to 70%.
Since tool changes, feeds, and speeds are pre-programmed, every production run is faster and more predictable. This makes CNC machining ideal for industries that demand quick turnaround — such as aerospace, medical, and electronics.
Cost-Effective Manufacturing
A CNC shop eliminates the need for in-house tooling investments, operator training, and machine setup costs.
Optimized tool paths reduce material waste, while simultaneous multi-axis machining shortens cycle times.
From low-volume prototyping to full-scale production, outsourcing to a CNC shop typically reduces total manufacturing costs by 20–40%.
Complexity And Flexibility
CNC machining can handle intricate designs that traditional methods cannot.
With flexible programming, engineers can easily switch between materials or modify designs without major downtime.
This versatility supports product customization, engineering changes, and continuous improvement, helping businesses stay competitive in fast-changing markets.
Common Operational Challenges
Running a CNC machine shop involves more than just precision cutting — it requires balancing efficiency, technology, and cost control. Despite modern automation, machining operations still face several challenges that affect production performance and profitability. Understanding these obstacles helps manufacturers improve workflow and ensure consistent quality.
1. High Initial Investment
Setting up a CNC machine shop demands significant capital. A single 5-axis machining center can cost between $150,000 and $500,000, excluding tooling, fixtures, and inspection systems. The cost of maintenance, software licenses, and skilled labor adds further financial pressure, especially for small manufacturers or startups.
2. Skilled Labor Shortage
While CNC machines automate production, they still rely on experienced machinists and programmers. The global shortage of skilled technicians leads to longer training cycles, potential errors, and production delays. Many shops invest in in-house training or hybrid automation systems to reduce dependence on manual programming.
3. Maintenance And Downtime
Continuous machine operation increases wear and tear. Unexpected breakdowns or tool failures can halt production for hours or days. Predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and regular calibration are essential to keep uptime above 95%.
4. Rapid Technological Changes
CNC technology evolves rapidly. Integrating newer systems such as AI-driven machining, IoT sensors, and advanced CAM software requires constant upgrades. Balancing innovation with cost control becomes a key management challenge for machine shop owners.
5. Quality Assurance And Inspection Time
As tolerance demands tighten, quality inspection becomes more complex and time-consuming. Achieving ±0.005 mm accuracy requires advanced tools like CMMs, optical scanners, and digital gauges, adding both cost and workflow bottlenecks.
Overcoming these challenges requires strategic planning — combining skilled personnel, predictive maintenance, and smart digitalization to maintain competitiveness and ensure long-term success.
How To Choose The Right CNC Machine Shop
Choosing the right CNC machine shop can determine the success or failure of your manufacturing project. A reliable partner ensures precision, cost-efficiency, and timely delivery — without the need for you to invest in costly in-house equipment. Here’s what you should look for before making a decision.
Capability & Tolerances; Sample Parts / Case Studies
Evaluate whether the shop has the right machinery and experience for your part requirements.
Check if they use 3-, 4-, or 5-axis machining centers, what tolerance levels they can maintain (typically ±0.01 mm or better), and what materials and surface finishes they support.
Ask for real sample parts or case studies demonstrating their experience in industries like automotive, aerospace, or medical. A proven track record is a strong sign of reliability and technical competence.
Quality System & Certifications
A professional CNC machining shop should have robust quality assurance systems.
Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, AS9100 (aerospace), or IATF 16949 (automotive).
These standards indicate the shop follows systematic inspection, documentation, and continuous improvement processes.
Also, ensure they provide inspection reports, CMM data, and material traceability to verify each order meets specifications.
Lead Time, Scalability & On-Time Delivery
Project deadlines are critical — a top-tier CNC shop should meet them consistently.
Ask about average lead times for prototypes (3–5 days) and production runs.
Assess whether they can scale up from small batches to mass production without delays.
Real-time order tracking and transparent communication are key indicators of a dependable manufacturer.
DFM Support & Transparent Pricing
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) support shows that the shop cares about your success.
Engineers who proactively review designs and suggest improvements can save both cost and production time.
Choose a shop that provides clear, itemized quotes — including machining, finishing, inspection, and shipping — to avoid hidden costs.
IP Protection & Communication
Confidentiality matters, especially for innovative products.
Ensure your chosen CNC machine shop has strict IP protection policies, NDAs, and controlled data management systems.
Effective communication — through email, instant messaging, or video calls — ensures smooth collaboration and quick response throughout production.
FAQs
What Does A CNC Machine Shop Mean?
A CNC machine shop is a precision manufacturing facility equipped with computer-controlled machinery for cutting, shaping, and finishing metal or plastic components. Using 3-, 4-, or 5-axis machining centers, it can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm, ensuring high accuracy for prototypes or mass production parts.
What Is The Hourly Rate For A CNC Machine?
The average hourly rate for CNC machining ranges between 60–150 USD, depending on machine type, part complexity, and material. 3-axis milling is typically around 60–90 per hour, while advanced 5-axis machining may cost 120–150 per hour due to higher setup and programming precision.
How To Get Reliable CNC Machine Shops?
To find a reliable CNC machine shop, I always evaluate five factors: machining capability, tolerance range, quality certification such as ISO 9001 or AS9100, on-time delivery rate, and DFM support. A trustworthy partner should provide inspection reports and case studies to prove past project success.
How Long Does CNC Machining Take?
Production time depends on design complexity, quantity, and finishing needs. Simple prototypes may take 2–5 days, while intricate 5-axis parts with anodizing or coating can require 1–2 weeks. High-volume orders benefit from automation, reducing lead time by up to 60 percent.
What Materials Can Be Machined In A CNC Shop?
CNC machine shops handle a wide range of materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, brass, and engineering plastics like PEEK or Delrin. Depending on hardness, cutting speed and feed rates are adjusted. Aluminum remains the most common, offering excellent machinability and cost efficiency.
Why Choose A CNC Machine Shop Over Manual Machining?
CNC machining provides superior accuracy and repeatability compared to manual methods. It reduces human error, increases efficiency, and maintains consistent tolerances up to ±0.005 mm. Additionally, automation allows continuous operation 24/7, improving production speed and cost-effectiveness by 30 to 40 percent.
What Quality Standards Do CNC Machine Shops Follow?
Top CNC machine shops comply with certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management, AS9100 for aerospace, and IATF 16949 for automotive. These ensure strict process control, inspection, and traceability. Shops also perform FAI, SPC, and MSA checks to maintain production accuracy.
What Services Do CNC Machine Shops Offer?
A CNC machine shop typically provides milling, turning, EDM, grinding, and surface finishing services. Many also offer design for manufacturability (DFM), assembly, and CMM inspection. This one-stop service structure allows efficient prototype development and scalable production for multiple industries.
How Does A CNC Machine Shop Ensure Precision?
Precision is achieved through digital programming, advanced cutting tools, and real-time monitoring. Machines operate within micron-level tolerance using feedback loops and temperature compensation. Regular calibration, CMM inspection, and tool wear analysis keep dimensional deviation below 0.01 mm.
How Can I Reduce CNC Machining Costs?
To minimize cost, I recommend simplifying designs, avoiding unnecessary tight tolerances, and selecting machinable materials like aluminum 6061. Ordering in batches and allowing flexible lead times can further reduce pricing by 20 to 30 percent. Always request a detailed DFM review before production.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive manufacturing environment, building an in-house CNC facility is often costly and inefficient. Partnering with an experienced CNC machine shop allows companies to leverage advanced equipment, skilled engineers, and standardized quality systems without large capital investment. This collaboration accelerates innovation, shortens product launch cycles, and ensures parts meet strict tolerances and certification requirements. By outsourcing precision manufacturing, businesses can focus their resources on design, R&D, and market expansion while achieving consistent, high-quality production results.




















