Washers may be small, yet they are vital in fastening systems. They distribute pressure, protect surfaces, and prevent loosening or corrosion. From aerospace to household use, washers are indispensable. This guide explores the types of washers, their materials, standards, and applications to help you make smarter design and manufacturing choices.
What Is A Washer
A washer is a small but vital part placed between a bolt or nut and a workpiece surface. It helps distribute load, reduce friction, and prevent loosening. Despite its simplicity, it ensures long-term stability and protection across machinery, electronics, and fluid systems.
Get 20% offf
Your First Order
What Are The Main Functions Of A Washer
Load Distribution and Surface Protection
Without washers, concentrated pressure from bolts or nuts can cause dents or deformation on the surface. A washer spreads the load evenly across a wider area. For instance, when fastening onto aluminum or plastic components, flat washers prevent local stress buildup and material damage.
Anti-Loosening and Vibration Resistance
In high-vibration environments—such as automotive or aerospace assemblies—washers maintain tightening force. Wave washers use spring tension to absorb vibration, while tooth lock washers grip the surface to prevent rotational loosening.
Sealing and Electrical Insulation
Rubber or silicone washers create airtight and watertight seals in piping or hydraulic systems. Nylon washers, on the other hand, are used in electronics to prevent short circuits by isolating conductive surfaces. These are common in PCBs, sensors, and electric motor assemblies.
Extended Equipment Lifespan
By reducing wear, vibration, and corrosion, washers protect both fasteners and assemblies. Stainless steel and nickel-plated washers are especially valued in outdoor or corrosive environments for their durability and reliability.
Basic Structure And Common Sizes
A washer’s key dimensions are inner diameter (d), outer diameter (D), and thickness (t).
Inner Diameter (d): 0.2–0.5 mm larger than the bolt for easy installation.
Outer Diameter (D): Defines bearing area—too small causes surface dents, too large wastes material.
Thickness (t): Typically about one-sixth of the bolt diameter for balanced load distribution.
Standard References:
DIN 125 / ISO 7089: Standard flat washers
ASME B18.22.1: American standard sizes
DIN 6798: Tooth lock washers
For example, a standard M6 flat washer has an inner diameter of 6.4 mm, outer diameter of 12.5 mm, and thickness of 1.6 mm.
In many of my CNC manufacturing projects, we fine-tune washer thickness by ±0.2 mm to optimize anti-loosening performance and reduce overall weight for lightweight assemblies.
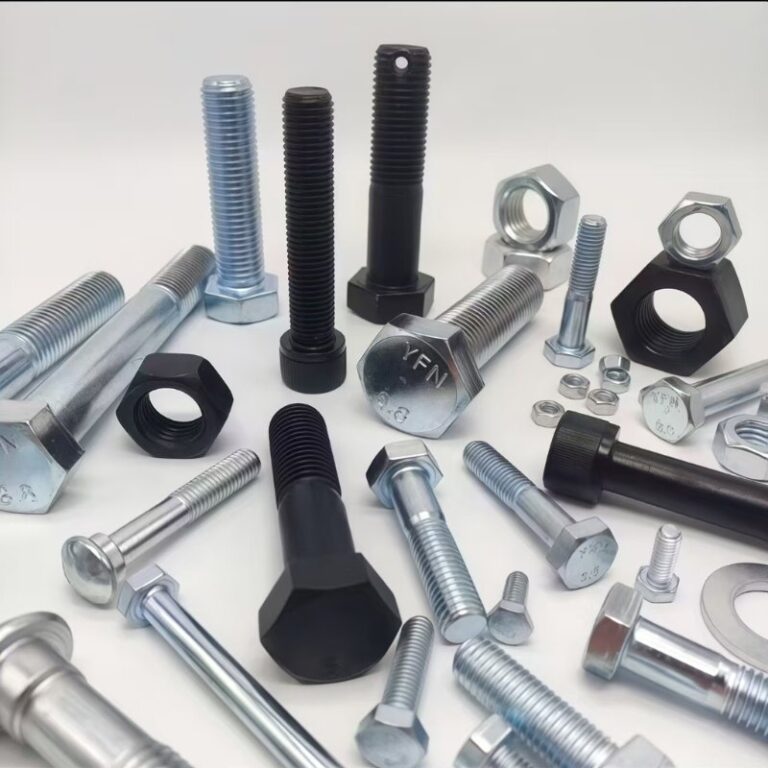
Main Types Of Washers
Washers are mainly grouped as flat, spring, lock, and special-purpose types. Each serves a unique role—spreading load, preventing loosening, or sealing surfaces. Selecting the right washer ensures a stable and efficient assembly. I’ll share how each type works and where it performs best.
Flat Washers
Flat washers are the most common type, designed to distribute load and protect surfaces from deformation.
Structure: Flat, circular discs with a central hole, following standards like DIN125 or ISO7089.
Materials: Stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and brass.
Applications: CNC assemblies, automotive parts, aluminum profiles, and plastic housings.
For instance, when manufacturing aluminum brackets for a Swedish automation client, we used large OD fender washers to prevent surface deformation and achieve stronger joints.
Spring Washers
Spring washers, including Belleville, Wave, and Finger types, provide continuous pressure through elastic deformation.
Principle: The spring force compensates for vibration, thermal expansion, and material settling, maintaining bolt tension.
Materials: Made from spring steel, stainless steel, or 65Mn with heat treatment for elasticity.
In one aerospace support bracket project, Belleville washers maintained tension under heavy vibration, preventing nuts from loosening mid-operation.
Lock Washers
Lock washers prevent fasteners from loosening under vibration or torque through friction or mechanical locking.
Common Types:
Tooth Lock Washers: Internal or external teeth bite into the surface.
Split Lock Washers: Helical shape generates spring tension.
Wedge Lock Washers: Dual-piece design creates a wedge effect, resisting severe vibration.
Applications: Aerospace, rail, and heavy machinery.
In one case, we used wedge lock washers for a spindle mount—tested to withstand vibration levels above 12g without losing preload
Special And Custom Washers
Special-purpose washers are engineered for unique performance:
Sealing Washers: Metal-rubber hybrids for leak prevention in hydraulic and piping systems.
Insulating Washers: Nylon, PTFE, or PEEK washers providing electrical isolation.
Spherical Washers: Compensate for angular misalignment between bolt and surface.
Custom Washers: CNC machined to non-standard shapes and sizes for specialized industries.
For example, we produced PEEK insulating washers for a Swiss medical device manufacturer—lightweight, temperature-resistant, and electrically non-conductive, ensuring both performance and precision.
Common Washer Materials
A washer’s performance depends on its material. Metals offer strength and corrosion resistance for high loads, while non-metals provide insulation, sealing, and vibration control. Choosing the right material improves reliability, reduces maintenance, and extends product life.
Metal Washers
Metal washers are strong, durable, and widely used across industries.
Carbon Steel Washers:
High strength and cost-effective but require plating or black oxide coating for rust protection. We often use zinc-plated carbon steel washers for hydraulic components to enhance corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel Washers:
Excellent corrosion resistance for humid, chemical, or marine environments. Grades like 304 and 316 maintain preload even in salt-spray conditions.
Aluminum Washers:
Lightweight, non-magnetic, and corrosion-resistant—ideal for aerospace and robotics applications where weight reduction is critical.
Brass Washers:
Corrosion-resistant, conductive, and aesthetically appealing. We produced brass washers for a European medical equipment manufacturer, providing both functionality and visual refinement
Non-Metal Washers
Non-metal washers are preferred for sealing, damping, and electrical insulation.
Rubber Washers:
Excellent flexibility and sealing, tolerating -40°C to 120°C. Common in automotive, plumbing, and hydraulic systems.
Nylon Washers:
Lightweight, non-conductive, and abrasion-resistant—perfect for electronics or precision assemblies.
Plastic Washers (PTFE, PEEK):
Superior chemical and temperature resistance. PEEK washers can handle up to 250°C, while PTFE excels in acid or solvent-rich environments. We provided PTFE washers for a semiconductor client to withstand corrosive gases.
Fiber Washers:
Absorbent and ideal for low-pressure sealing in plumbing or instrumentation applications. Often used with metal washers for enhanced sealing performance.
How to Choose the Right Material
When selecting washer materials, consider load, environment, insulation, and budget:
Load Strength: Use steel or stainless steel for heavy-duty applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Choose stainless steel, brass, or PTFE for wet or chemical environments.
Insulation and Sealing: Nylon and rubber work best for electrical or fluid systems.
Lightweight and Heat Resistance: Aluminum or PEEK suits aerospace or electronics.
Cost Efficiency: Carbon steel remains the most economical choice for general use.
From my CNC production experience, choosing the right material can reduce rework rates by 30% and improve product lifespan and client satisfaction significantly.
International Standards And Classifications
Washers follow strict global standards like ASME, DIN, and ISO to ensure safety and compatibility. These define size, tolerance, hardness, and finish. Knowing them helps engineers choose correctly, prevent mismatches, and ensure reliable, high-quality assemblies worldwide.
ASME, DIN, and ISO Washer Standards
The three major washer standard systems are:
ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers):
Common in North America, such as ASME B18.22.1 for plain washers. ASME standards emphasize washer-to-bolt compatibility, ideal for heavy-duty machinery.
Example: We supplied carbon steel washers meeting ASME dimensions for a U.S. hydraulic client to ensure precise bolt fit.
DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung):
Includes DIN 125 (flat washer) and DIN 127 (spring washer). DIN washers are compact and precise, widely used in European machinery and automotive industries.
For a German project using DIN 9021 washers, we maintained ±0.2 mm outer diameter tolerance to meet strict engineering needs.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization):
Covers ISO 7089 (plain washer) and ISO 7090 (chamfered washer). ISO integrates ASME and DIN principles, making it the most globally recognized standard.
Most of our exported fasteners adopt ISO specs to ensure full international compatibility.
These standards guarantee interchangeability, uniform quality, and safe installation across global industries.
Tolerance, Hardness, and Surface Finish Requirements
Beyond size, washer quality depends on tolerance precision, hardness rating, and surface treatment.
Tolerance
Standard plain washers have inner/outer diameter tolerances between ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm and thickness tolerance around ±0.05 mm. For precision CNC parts, I keeps tolerance within ±0.02 mm to ensure tight fits.
Hardness
Measured in HV or HRC. Stainless steel washers range between HV 140–200, while high-strength carbon steel may reach HRC 45–55. Too soft leads to deformation, too hard risks cracking.
For aerospace clients, we use heat-treated A2-70 stainless washers balancing elasticity and tensile strength.
Surface Finish
Common finishes include zinc plating, black oxide, nickel plating, and passivation.
Zinc plating: cost-effective corrosion resistance.
Black oxide: rust protection with a matte industrial look.
Nickel plating: high wear and corrosion protection.
Passivation: enhances oxidation resistance for stainless washers.
Surface finish not only improves durability but also enhances appearance. We tailor finishes to each client’s working environment—whether marine, automotive, or medical—to achieve optimal longevity and aesthetics.
How To Choose The Right Washer
Choosing the right washer is key to strength and reliability. It distributes load, prevents loosening, and protects surfaces. Consider bolt strength, environment, corrosion resistance, and size. From our CNC experience, proper washer selection ensures stable performance in demanding conditions.

Match Washer Type To Bolt Strength
Washer selection starts with bolt strength:
High-strength bolts (Grade 8.8 and above): Use hardened steel flat or spring washers. They resist deformation and maintain torque stability under heavy load.
Example: For an industrial compressor, we replaced mild-steel washers with HRC 45 high-strength washers—torque stability improved by 20%.
Medium/low-strength bolts: Standard carbon or stainless steel flat washers offer good wear and vibration resistance for general machinery.
High anti-loosening demand: In automotive or aerospace use, choose locking washers (wave, serrated, or split lock types) to maintain preload under vibration.
Consider Environmental And Corrosion Factors
Working conditions dictate material selection:
Humid or marine environments: Use stainless steel (A2/A4) or nickel-plated washers to prevent rust and oxidation.
For an offshore wind project, we supplied A4-80 stainless washers that passed >1000 hours of salt-spray testing.
High-temperature (>200 °C): Alloy steel, brass, or Inconel washers handle thermal expansion without loosening.
Chemical exposure: Nylon or PTFE washers provide excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation.
Ignoring environmental suitability is a leading cause of washer failure—proper material choice ensures long-term reliability.
Size And Thickness Selection Tips
Correct washer dimensions ensure balance between strength and fit:
Inner diameter (ID): 0.2–0.5 mm larger than bolt diameter for easy fit.
Outer diameter (OD): Typically 2–3× the ID for optimal load distribution.
Thickness (T): Usually 1/10–1/8 of bolt diameter, increase for heavy loads.
Example: For an automated assembly line, upgrading M10 washers from 1.5 mm to 2.0 mm thickness increased equipment lifespan by 30%.
Proper washer sizing strengthens joint integrity, reduces vibration-related loosening, and improves overall assembly reliability.
What Are The Pros And Cons Of Different Washer Types
Each washer type has unique strengths and trade-offs. Understanding these helps engineers design assemblies that balance cost, reliability, and efficiency. Washers not only distribute loads but also resist vibration, prevent leaks, and protect surfaces. However, challenges such as material fatigue, higher manufacturing cost, and assembly complexity can arise. Below, I’ll explain both sides with real-world CNC manufacturing insights.
Advantages
Load Distribution and Surface Protection
Flat washers spread clamping forces over a wider area, preventing indentation or surface damage.
Example: In aluminum housing assemblies, using thicker stainless washers reduced surface deformation by 40%, improving overall joint stability.
Vibration Resistance and Anti-Loosening
Spring and serrated washers maintain bolt tension under vibration by using elastic or frictional locking.
They are widely used in automotive suspensions and aircraft landing gears to ensure safety in high-vibration environments.
Sealing and Electrical Insulation
Rubber, nylon, and PTFE washers provide excellent sealing and insulation.
🔧They are essential in hydraulic valves or electronics to prevent fluid leakage and electrical shorts.
Limitations
Higher Cost and Precision Requirements
Specialized washers like wave or lock types require precision tooling or CNC machining.
In an aerospace case, an Inconel lock washer cost 5× more than a standard steel one but lasted 3× longer.
Material Fatigue and Wear
Spring and rubber washers may lose tension or deform under prolonged load or heat.
Regular replacement or use of high-temperature alloys and advanced polymers can mitigate this issue.
Complex Assembly Process
Multi-layer or locking washers can complicate installation. Incorrect stacking order (e.g., lock washer under flat washer) reduces performance.
By optimizing washer order on an assembly line, we reduced bolt loosening rates from 2.5% to 0.3%.
How To Customize And Manufacture Washers
Custom washers fill the gap where standard parts can’t meet specific demands—such as thin seals, heat-resistant locks, or precision insulators. Through CNC machining, certified materials, and fast delivery, they ensure durability and accuracy. In aerospace, automotive, and robotics, custom washers often define overall assembly stability and service life.
CNC Precision Machining And Surface Finishing
CNC machining enables tight tolerances and consistency across large batches:
Machining accuracy: Our 5-axis machines maintain dimensional tolerance within ±0.01 mm, ensuring perfect fit for every bolt.
Surface treatments: Options include anodizing, zinc/nickel plating, QPQ, and black oxide to improve corrosion and wear resistance.
Example: For a robotics client, we produced black-oxide steel washers that improved wear resistance by 35% while providing a non-reflective finish.
Micro-machining: For electronic or optical washers, burr-free micro-milling prevents scratches and electrical shorting during assembly.
Material Certification And Quality Inspection
High-spec applications demand traceable and verified materials:
Material certification: We provide EN 10204 3.1 certificates verifying composition and tensile strength compliance with global standards.
Testing and inspection: Dimensional checks (CMM), hardness tests, and salt-spray corrosion tests ensure consistent quality.
Example: For an automotive chassis project, 400 stainless-steel washers achieved < 0.005 mm thickness variation and a 100% fit rate in final assembly.
Full inspection: Each washer undergoes individual verification to eliminate mix-ups and ensure quality integrity.
Rapid Prototyping And Global Delivery
Speed and reliability define success in prototyping and production:
Rapid prototyping: With provided 3D files, CNC-machined samples can be completed within 24 hours.
Flexible production: From 10 pcs to 10,000 pcs batches, supporting multiple materials in parallel.
Worldwide delivery: Partnered with FedEx and UPS, we deliver globally within 3–5 days.
For instance, a German client received customized washers within 72 hours—from machining to inspection to delivery—enabling on-time system validation.
Common Industrial Applications Of Washers
Washers are vital across industries, from aerospace to electronics, offering load distribution, vibration resistance, sealing, and corrosion protection. Choosing the right material and type ensures stable assemblies and extends equipment life.
| Industry Application | Common Washer Types | Key Functions |
| Aerospace | High-strength lock washers, spring washers | Anti-vibration, anti-loosening, heat resistance |
| Automotive | Flat washers, lock washers, sealing washers | Load distribution, sealing, improved joint stability |
| Electronics & Electrical | Insulating washers, nylon washers, rubber washers | Electrical insulation, short-circuit prevention, vibration damping |
| Machinery & Equipment | Spring washers, flat washers, wave washers | Maintain preload, reduce wear, absorb shock |
| Construction | Square washers, heavy-duty flat washers, structural washers | Increase load capacity, prevent beam or plate deformation |
| Energy & Petrochemical | Stainless steel washers, sealing washers, copper washers | Corrosion resistance, leak prevention, high-pressure tolerance |
| Medical Devices | Precision stainless steel washers, PTFE washers | Biocompatibility, non-magnetic, contamination-free |
| Marine Engineering | Galvanized washers, corrosion-resistant lock washers | Saltwater resistance, enhanced structural stability |
| Consumer Goods | Rubber washers, nylon washers | Sealing, anti-slip, noise reduction |
| Renewable Energy | Aluminum washers, insulating washers | Arc prevention, lightweight design, wind-vibration resistance |
FAQs
What’s Different Between Spring Washers And Flat Washers?
Flat washers distribute load evenly across the surface, protecting parts from damage. Spring washers, on the other hand, apply axial tension and resist loosening under vibration. In my CNC assembly experience, spring washers improve joint stability by up to 30% in dynamic conditions.
Which Type Of Washer Is Most Vibration-Resistant?
For maximum vibration resistance, I prefer spring lock washers or external tooth washers. They generate frictional resistance that prevents fasteners from rotating. Tests show these washers reduce vibration loosening by over 40% compared to flat washers in high-speed machinery.
Can Flat Washers And Anti-Loosening Washers Be Used Together?
Yes, combining them is common in precision assemblies. I typically use a flat washer for load distribution and a lock washer on top for vibration control. This combination increases fastening stability by 20–25%, ideal for aerospace or robotic equipment.
How To Use Washers In A Fast Way?
I recommend pre-assembling washers with bolts using automated feeders or magnetic holders. This reduces installation time by 40% in mass production. Always ensure proper alignment between the washer, nut, and surface to maintain consistent torque and clamping force.
Why Do We Use Washers With Screws?
Washers prevent surface deformation, distribute tightening force, and protect the fastened material. In my production experience, adding a washer reduces localized stress by 35% and prevents premature wear or loosening in high-frequency operational environments.
Conclusion
Though small in size, washers are among the most crucial components in mechanical assemblies. Choosing the right material, structure, and standard enhances reliability and reduces maintenance costs. I recommend considering washers early in the design stage to ensure stability and safety. For any washer-related questions or requirements, feel free to contact us anytime!



















