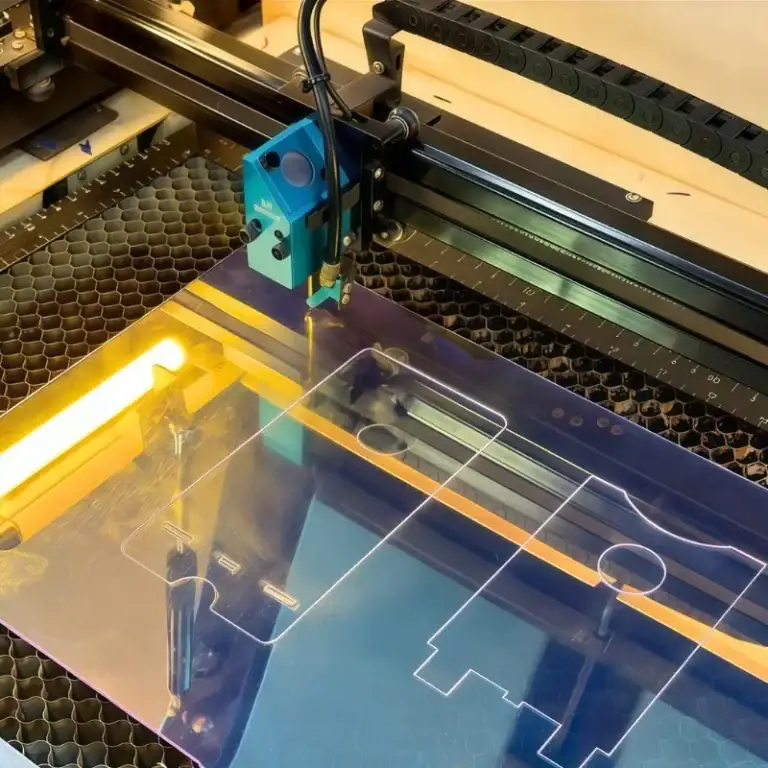
Aluminum prototypes are essential in modern product development, allowing engineers to verify form, fit, and function using a material close to final production parts. With CNC machining, these prototypes can be produced quickly, accurately, and with high repeatability for functional and pre-production testing.
This article explains how CNC machining creates aluminum prototypes, why aluminum is widely used, and how it bridges the gap between concept and production.
What Are Aluminum Prototypes
Aluminum prototypes are functional sample parts manufactured from aluminum alloys through CNC machining manufacturing to verify design, performance, and manufacturability before full-scale production. Compared to plastic prototypes, aluminum parts provide higher strength, better thermal stability, and more realistic mechanical behavior.
Get 20% offf
Your First Order
What Are the Common Methods for Making Aluminum Prototypes
Aluminum prototypes are commonly produced using CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, aluminum casting, and metal 3D printing, depending on design complexity, accuracy requirements, quantity, and lead time.
The most common methods include:
CNC Machining
CNC machining is the most widely used method for aluminum prototyping because it delivers the highest level of accuracy and consistency. It is especially suitable when prototypes must closely match final production parts.

Key characteristics include:
- High dimensional accuracy: Typical tolerances of ±0.01–0.05 mm, ideal for functional testing and assemblies
- Excellent surface quality: Smooth finishes achievable directly from machining, with optional post-processing
- Wide alloy compatibility: Commonly used alloys include 6061, 7075, and 5052
- Production-like behavior: Mechanical strength, thermal performance, and weight closely reflect end-use parts
CNC machining is best for engineering validation, fit-and-function testing, and low-volume pre-production parts.
Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is a fast and cost-effective prototyping method for aluminum parts with thin walls or enclosure-style designs.
Typical applications include:
- Thin-wall components: Panels, brackets, housings, and covers
- Processes used: Laser cutting, bending, punching, and simple welding
- Short lead times: Flat parts and simple bends can be produced very quickly
- Lower tooling cost: No complex molds or fixtures required
However, sheet metal fabrication is limited in geometry complexity and is not suitable for thick, highly contoured, or precision-machined parts.
Aluminum Casting
Aluminum casting is commonly used when prototypes need to simulate final cast components, especially for shape evaluation rather than tight tolerance testing.
Key features include:
- Complex geometry capability: Suitable for parts with internal cavities or organic shapes
- Near-production simulation: Helps evaluate mold design, wall thickness, and overall form
- Lower machining requirement: Minimal CNC machining may be used for critical surfaces
Casting prototypes typically have lower dimensional accuracy and rougher surface finishes compared to CNC machining, making them less suitable for precision functional testing.
Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing enables rapid creation of aluminum prototypes with complex internal features that are difficult or impossible to machine.
Main advantages include:
- Design freedom: Internal channels, lattice structures, and lightweight designs
- No tooling required: Ideal for early-stage concept validation
- Fast design iteration: Changes can be made directly from CAD models
Limitations include higher cost, rougher surface finish, and lower dimensional precision compared to CNC machining. As a result, metal 3D printing is often used for design verification, not final functional testing.
In practice, CNC machining remains the preferred choice for aluminum prototypes when parts must closely match final production in material behavior, tolerance, and performance. Other methods such as sheet metal fabrication, casting, and metal 3D printing are valuable at specific stages—but CNC machining provides the best balance of accuracy, speed, and reliability for most engineering prototypes.
What Aluminum Materials Are Used for Prototyping
Choosing the right aluminum alloy, such as 6061 or 6063, is essential for prototype development. Different alloys vary in strength, machinability, corrosion resistance, and cost, helping prototypes reflect final production performance.
| Aluminum Alloy | Key Properties | Machinability | Typical Prototype Applications |
| 6061 | Balanced strength, good corrosion resistance, stable dimensions | Excellent | General mechanical parts, structural prototypes, housings, functional testing |
| 6063 | Good surface finish, moderate strength, excellent extrudability | Excellent | Enclosures, frames, cosmetic prototypes, architectural parts |
| 7075 | Very high strength, fatigue resistant, aerospace-grade | Good | Aerospace components, motorsport parts, high-load structural prototypes |
| 5052 | Excellent corrosion resistance, good formability | Moderate | Sheet metal enclosures, covers, lightweight casings |
| 2024 | High strength and fatigue resistance, lower corrosion resistance | Fair | Aerospace structures, load-bearing prototypes, fatigue-critical parts |
What Surface Finish Options Are Available for Aluminum Prototypes
Aluminum CNC prototypes can be finished using anodizing, bead blasting, and polishing, depending on whether the focus is corrosion resistance, surface durability, or visual appearance. These surface treatments help simulate final production conditions and support functional testing, aesthetic evaluation, and pre-production validation.

Anodizing
- Anodizing forms a protective oxide layer on aluminum surfaces.
- Significantly improves corrosion and wear resistance
- Allows color options for identification or aesthetics
- Enhances surface hardness without affecting core material
- Common for functional testing and pre-production evaluation
Clear anodizing is widely used for dimensional stability, while colored anodizing is often chosen for visual differentiation.
Bead Blasting
- Bead blasting uses fine media to create a uniform matte surface.
- Produces consistent, non-reflective surface texture
- Hides minor machining marks and tool paths
- Improves visual quality for customer review or presentation
- Often used as a pre-treatment before anodizing
Bead blasting is commonly applied when both appearance and surface uniformity are important.
Polishing
- Polishing enhances surface smoothness and visual appeal.
- Reduces surface roughness for improved fit or sealing
- Creates a smooth or mirror-like finish when required
- Useful for visible components or demonstration prototypes
- Can improve cleaning and contamination resistance
Polished finishes are often used for consumer-facing parts or high-precision mating surfaces.
Which Industries Use Aluminum Prototypes
Aluminum CNC prototypes are widely used in aerospace, automotive and motorsport, consumer electronics, medical devices, and industrial equipment for early design validation, functional testing, and pre-production evaluation.

Aerospace and Aviation Components
In aerospace applications, aluminum CNC prototypes are used to validate lightweight, high-strength parts such as brackets, housings, and mounting components. Prototyping helps engineers confirm dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and assembly fit before moving to production.
Automotive and Motorsport Parts
Automotive and motorsport teams use aluminum CNC prototypes to test performance-driven components like engine parts, suspension brackets, and custom racing components. Fast turnaround and high repeatability support rapid iteration during pre-production and competitive development.
Consumer Electronics Housings
In consumer electronics, aluminum CNC prototypes are commonly used for device enclosures, frames, and heat-dissipation parts. These prototypes allow teams to evaluate appearance, ergonomics, thermal performance, and assembly quality before mass production.
Medical and Industrial Equipment
Aluminum CNC prototypes support functional testing for medical and industrial components such as device housings, fixtures, and precision mechanical parts. CNC machining ensures consistent accuracy for repeated testing and early compliance evaluation.
| Industry | Typical Aluminum CNC Prototype Parts | Key Validation Goals |
| Aerospace & Aviation | Structural brackets, housings, mounts | Weight reduction, precision, assembly fit |
| Automotive & Motorsport | Engine parts, suspension brackets, enclosures | Performance testing, rapid iteration |
| Consumer Electronics | Device housings, frames, heat sinks | Appearance, thermal performance, ergonomics |
| Medical Equipment | Device housings, fixtures, precision components | Reliability, accuracy, compliance readiness |
| Industrial Equipment | Automation parts, mechanical assemblies | Durability, repeatability, functional testing |
FAQs
Is Aluminum A Common Prototyping Material?
Yes. Prototype aluminum is widely used in aluminum prototype manufacturing because it machines easily and performs close to final production materials. In our shop, aluminum CNC machining prototypes are often chosen for fast form, fit, and function validation.
How Does Aluminum Prototype Machining Benefit Aerospace Applications?
Aluminum prototype machining helps aerospace teams test lightweight structures and assembly fit. We commonly produce aluminum CNC prototypes to evaluate strength, weight, and performance before production.
Why Is CNC Machining Preferred For Aluminum Prototypes?
We prefer aluminum CNC machining prototypes because CNC machining delivers higher accuracy than aluminum prototype metal stamping or casting. CNC aluminum parts prototypes closely match final production geometry and performance.
How Do We Control Heat During Aluminum Prototype Machining?
During aluminum prototype machining, we control heat through optimized cutting parameters and effective coolant use. This ensures stable quality and dimensional accuracy in CNC aluminum prototype projects.
Conclusion
Aluminum prototypes play a critical role in product development by enabling accurate form, fit, and function validation. Among all methods, CNC machining offers the best balance of precision, material realism, and repeatability, making it the preferred solution for functional testing and pre-production verification across multiple industries.
At TiRapid, we specialize in aluminum CNC prototypes with tight tolerances, production-grade materials, and fast turnaround. Upload your drawings to get a reliable CNC aluminum prototype service today.